Unleashing the Secrets of Mouse Tails: A Game-Changer in Balance and Neurodegenerative Disease Research!
2024-11-06
Author: William
What if I told you that one of the smallest features of a mouse—their tail—could unlock groundbreaking insights into human health? Recent research from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) is shifting our understanding of these furry creatures and their crucial role in maintaining balance.
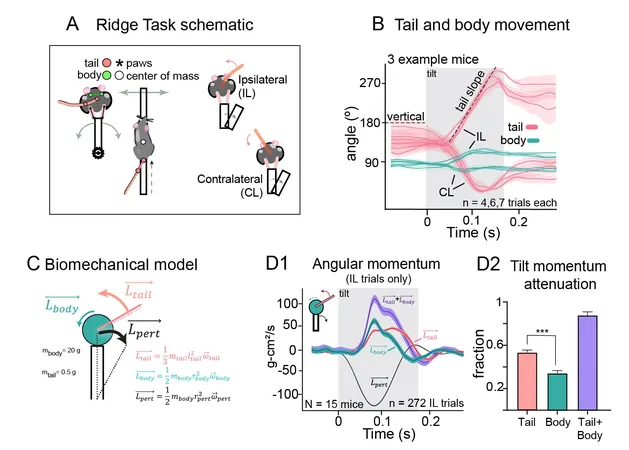
The talented team of scientists utilized an innovative experimental design that included a tilting platform, high-speed cameras, and mathematical modeling to reveal new perspectives on how mice use their tails to keep their footing. This revelation could lead to earlier detection and treatment strategies for neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and multiple sclerosis.
Dr. Salvatore Lacava, a leading researcher in the Neuronal Rhythms in Movement Unit at OIST, noted the unexpected findings about mice tails: “Their tails are not merely a passive counterweight; instead, they actively engage to help the mice maintain balance.” When faced with a tilting surface, mice quickly rotate their tails in the opposite direction to counteract shifts in their center of gravity.
Imagine this: if you could whip your body in the direction of the crack of a whip, instantly preventing yourself from falling! That’s the power of the mouse’s tail. Furthermore, researchers discovered that the tail is essential for traversing narrow platforms too, continuously adjusting to keep the mouse steady while moving.
This groundbreaking study challenges conventional wisdom—not only shedding light on an overlooked aspect of mouse locomotion, but also offering a new model to detect balance issues in research settings. Professor Marylka Yoe Uusisaari emphasized the importance of this study by saying, “Mice’s tails may not seem relevant to human health, but they provide essential insight into conditions impacting motor control.”
The researchers also devised a new experimental framework to more accurately assess balance. Traditional tests usually involve mice walking across a 1cm-wide beam, but this was inadequate for assessing the more intricate balance needed for mice adept at darting across narrow branches in their natural habitats. Their new approach features varying platform widths—from a daunting 4mm to 1cm—along with unpredictable 10 to 30-degree tilts. This setup presents a far more realistic and challenging scenario for the mice, allowing for a deeper understanding of their balance capabilities.
To track the tiny movements of the mice and further this understanding, the research team developed a biomechanical model powered by a neural network. This model details the intricate motion mechanics, including how the motion of the tail provides counterbalance. Dr. Lacava hopes that such advancements in research will empower early detection and treatment of balance-related issues in humans before they result in significant mobility challenges.
The research clearly indicates that by examining the seemingly simple aspects of mouse anatomy, scientists can glean vital information essential for exciting advancements in healthcare. As we delve deeper into the science behind balance, the mystery of the mouse tail continues to unravel with potentially life-changing implications for human health. Are you ready to follow this tail down the path of discovery?








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)