The Alarming Link Between Inflammation, Depression, and Stroke Risk: New Insights from NHANES
2025-09-13
Author: Benjamin
Understanding the Hidden Dangers of Depression and Inflammation
Recent research reveals a shocking connection between depressive symptoms, inflammation levels, and serious health risks like stroke and major cardiovascular events. The study, leveraging data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning 2005 to 2018, sheds light on how our emotional well-being can directly impact our physical health.
What is Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR)?
The Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) is a marker of inflammation in the body, reflecting the balance between two immune cell types. High NLR levels indicate greater systemic inflammation, which has been associated with a higher risk of various health issues, including stroke and mortality.
The Research Unveiled: Key Findings
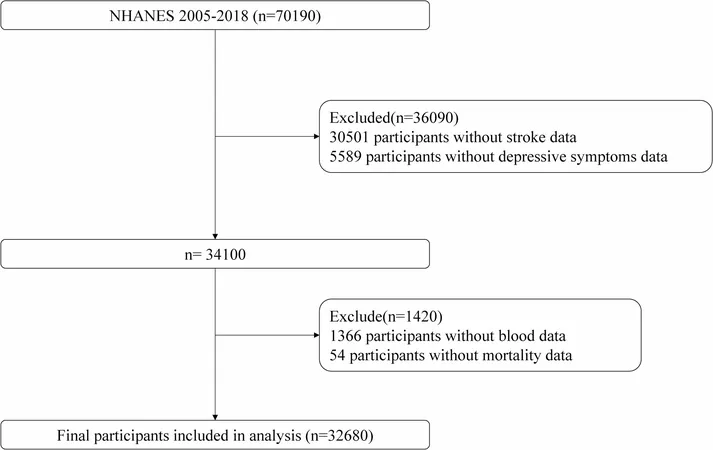
The study analyzed data from 32,680 participants, focusing on their NLR and scores from the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), which gauges depressive symptoms. Findings revealed that higher NLR and PHQ-9 scores corresponded to a significantly increased risk of stroke and overall mortality.
Participants with elevated NLR levels showed a 40% increased risk of dying from any cause and an almost 93% higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Those scoring 10 or more on the PHQ-9 were at an even greater risk, with mortality rates skyrocketing.
The Disturbing Interplay: How Inflammation Mediates Health Risks
What's particularly alarming is how NLR mediates the relationship between depressive symptoms and these health risks. The research indicates that inflammation not only results from severe depression but may also aggravate health conditions such as stroke and cardiovascular issues. About 5.9% of the link between depression and mortality was attributed to NLR levels.
Why This Matters: The Global Health Challenge of Stroke
Stroke isn't just a personal health issue; it's a pressing global health crisis, ranking among the top causes of death and disability worldwide. The study underscores the urgent need for healthcare strategies that address not just physical but mental health as well, integrating mental health screenings in routine health evaluations.
The Ripple Effect: How Depression Affects Physical Health
Depression is a primary cause of mental health-related disability globally, with its prevalence on the rise. The debilitating effects of depression can activate inflammatory responses, which further increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. These insights suggest that addressing mental health may be key to mitigating physical health risks.
Moving Forward: Recommendations for Health Care
Healthcare providers should consider comprehensive approaches that address both inflammation and mental health in treating patients. Early identification of depressive symptoms, alongside inflammatory markers like NLR, could be crucial in preventing strokes and improving overall health outcomes.
Final Thoughts: Holistic Health is Vital
This study not only explores the link between depression and inflammation but also opens new avenues for understanding how interconnected our mental and physical health truly are. Tackling inflammation could unlock new pathways for preventing one of the most significant health threats of our time — stroke.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)