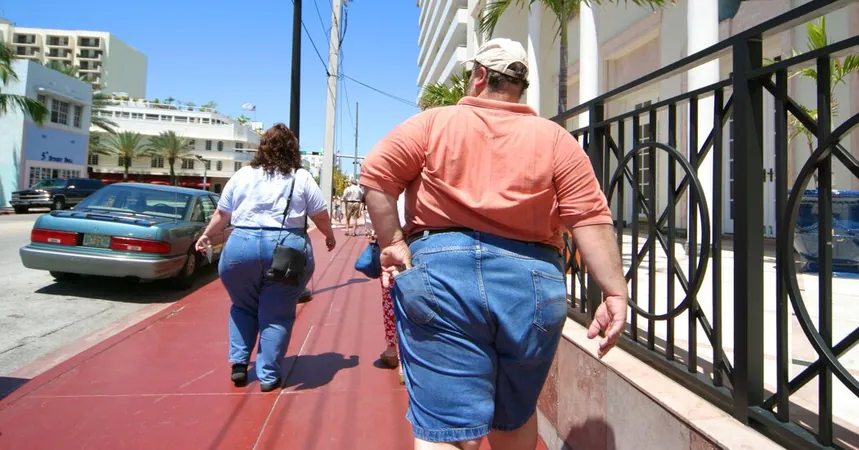

Shocking Statistics Reveal Nearly 75% of U.S. Adults Struggle with Obesity!
2024-11-15
Author: Michael
Introduction
In a startling revelation, a comprehensive new study has found that close to three-quarters of U.S. adults are now classified as overweight or obese, prompting serious concerns regarding the nation's health and financial burdens associated with weight-related diseases. Published in *The Lancet* on Thursday, the study marks a dramatic increase in obesity rates across the United States since 1990, when just over half of adults fell into these categories.
Trends and Health Risks
Among the most alarming trends identified is the fact that more individuals are experiencing weight struggles at younger ages than in previous generations. This shift raises urgent health issues, as obesity is associated with increased risks of severe conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and significantly shortened life expectancy.
Rising Rates Among Children and Predictions
The researchers documented a troubling rise in these rates across all age groups, particularly among children. Statistically, over one-third of American children are now deemed overweight or obese. Without immediate action, experts predict that the number of overweight and obese individuals could soar to nearly 260 million by 2050.
Experts Weigh In
Dr. Marie Ng, a co-author and associate professor at the Institution for Health Metrics and Evaluation, referenced this issue as an "epidemic," emphasizing the need for "major reform" to tackle the escalating crisis. Dr. Sarah Armstrong, a pediatric and population health sciences professor, echoed these sentiments, calling for heightened attention and resources to effectively combat the problem.
Defining Overweight and Obesity
The study follows a specific definition of "overweight" for adults aged 25 and over with a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 25 or higher, and "obese" individuals as those with a BMI of 30 or above. While BMI is recognized as an imperfect measure, it correlates with body fat and is a practical tool for population-level studies.
Economic Implications
The findings uncovered a shocking trend: the obesity rate among adults has doubled since 1990, hitting over 40 percent, while the rate among girls and young women aged 15 to 24 has nearly tripled to 29 percent. Economically, the Joint Economic Committee Republicans reported that obesity will likely lead to up to $9.1 trillion in excess medical costs over the next decade.
Complex Causes of Obesity
As our understanding of obesity evolves, it is clear that the causes are not simply rooted in individual calorie consumption. Instead, it is influenced by a complex interplay of genetic, physiological, and environmental factors. These include the overwhelming availability of ultra-processed foods, limited access to fresh produce, and an increasingly sedentary lifestyle driven by technology.
Impact on Marginalized Communities
A spotlight is also shining on the increased prevalence of obesity among marginalized communities such as Black, Hispanic, and Indigenous populations, who are disproportionately affected due to socio-economic factors like food insecurity, transportation, income, employment, and education.
Rising Rates Among Adolescents
Particularly concerning is the rising rate of obesity among adolescents. Almost half of U.S. teens and young adults (ages 15 to 24) are now either overweight or obese—a significant increase from 29 percent in 1990. This trend brings long-term health risks, as children facing obesity are more likely to develop serious conditions that can carry into adulthood.
Towards Solutions
Dr. Sarah Hampl, a pediatric expert, stated that addressing obesity involves a multifaceted approach including lifestyle changes, medications, and potentially surgery, while stressing the importance of adequate insurance coverage for effective treatments. New medications like GLP-1 drugs show promise, yet their long-term effects and accessibility remain uncertain.
Recommendations for Action
To reverse these alarming trends, experts argue for structural changes, such as subsidies for healthier food options and taxes on sugary beverages. Furthermore, implementing stricter regulations on food marketing and nutritional content is deemed essential for fostering healthier dietary habits at a national scale.
Conclusion
As we inch closer to a saturation point, with rates reaching potentially 80 percent, the implications for public health are profound. Experts warn that without immediate, coordinated action at the federal level, the situation is unlikely to improve, leaving millions of Americans at a greater risk for preventable diseases and a diminished quality of life. The fight against obesity is a battle we must take seriously—our future depends on it!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)