
**Scientists Unearth Alien-Like Flatworm Eggs at 20,300 Feet: A Deep Sea Discovery That Shatters Records!**
2025-09-16
Author: Charlotte
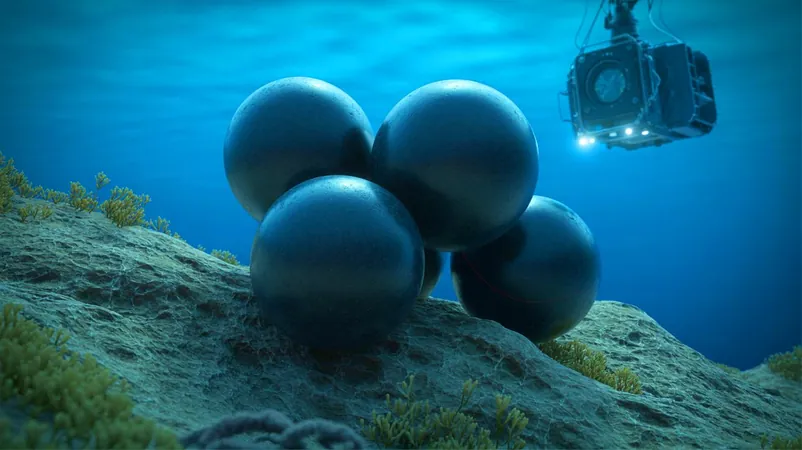
In an eye-opening revelation, researchers have stumbled upon enigmatic black egg capsules nestled at an astonishing depth of 20,300 feet in the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench. This groundbreaking find not only marks the deepest reproduction documented for free-living flatworms but also revolutionizes our comprehension of life in extreme oceanic realms.
**The Deepest Flatworm Reproduction Ever Documented!**
Led by scientists from the University of Tokyo and Hokkaido University, this remarkable expedition utilized a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) to discover four gleaming black spheres clinging to a rocky surface. Initially mistaken for fish eggs, these striking capsules were later confirmed to be cocoons of free-living platyhelminths—a type of flatworm typically found in shallow tide pools, not the crushing depths of the ocean.
Inside each capsule, researchers found three to seven embryos at various stages of development, some looking like tiny spheres while others had transformed into elongated, worm-like shapes. These capsules contained a milky fluid and delicate white bodies. Invertebrate biologist Kakui remarked, "I had never seen flatworm cocoons before," emphasizing the novelty of this discovery.
**What These Embryos Reveal About Extreme Ocean Life**
Genetic analysis of the embryos connected them to the Tricladida order, specifically falling under the Maricola suborder. These marine flatworms are generally found in coastal regions, indicating they likely descended from shallower waters rather than evolving in the deep sea. This finding aligns with recent studies suggesting that many deep-sea species have ancestors that originated from shallower ecosystems.
This evolutionary journey points to the idea that adapting to extreme environments like the hadal zone doesn't necessarily demand drastic bodily changes. Instead, the focus is on physiological endurance. The embryos displayed no unusual larval forms or adaptive unique traits, resembling their shallow-water cousins.
**The Abyss: A Hidden Cradle of Biodiversity**
The Kuril-Kamchatka Trench, stretching over 31,000 feet deep, remains largely unexplored, but the site of these egg capsules—the abyssal slope—spans from 11,300 to over 20,000 feet. This corridor likely harbors an incredibly rich yet undocumented biosphere.
Since deep-sea organisms are so fragile, most documentation methods can severely damage specimens. However, the intact egg capsules offer an unprecedented view into early developmental stages, serving as a crucial piece of the puzzle for understanding species survival in these depths.
**The Significance of Flatworms in Science**
Despite their simplicity, free-living flatworms intrigue scientists due to their remarkable regenerative capabilities, allowing them to restore entire body parts. This makes them extraordinary models for studying morphogenesis, cell differentiation, and resilience under stress.
By marrying field collection data with molecular analysis, this study sets the stage for forthcoming surveys and advancements in ROV technology. Genetic tools are vital for mapping biodiversity in remote, inaccessible environments, and each new discovery enhances our understanding of these hidden ecosystems.
As scientists delve deeper into the mysteries of the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench and beyond, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries is limitless. Will these insights reshape our understanding of life in extreme conditions and the resilience of Earth's simplest beings? Stay tuned for more!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)