Revolutionary AI Technology Can Gauge Infant Brain Maturity in Just Minutes!
2025-05-27
Author: Michael
Unlocking the Secrets of Infant Brain Development
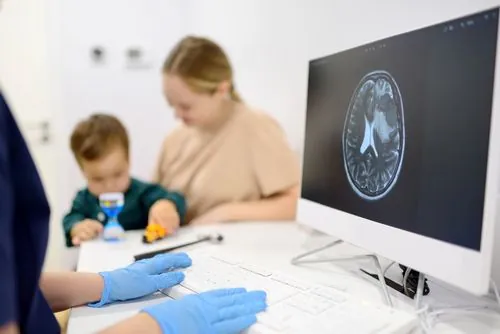
In a groundbreaking advancement, machine-learning algorithms are now capable of precisely estimating the 'brain age' of infants by analyzing electrical brain signals through electroencephalography (EEG). This innovative technique can assess whether an infant's brain development is ahead of schedule, on track, or falling behind—all within mere minutes!
Transforming Early Identification of Developmental Disorders
Led by the brilliant Sarah Lippé at the Université de Montréal’s Department of Psychology, this method not only promises rapid assessments but also introduces the potential for early screening and personalized monitoring of developmental disorders in young children. "The early years are crucial for brain development," emphasizes Lippé, highlighting the need for effective tools that can identify children at risk for conditions like language delays, attention deficit disorder, and autism.
A Game-Changing Study Involving 272 Babies
The team conducted an in-depth study involving 272 infants, including 53 with macrocephaly—a condition linked to atypical brain development. Under Lippé’s guidance, PhD student Saeideh Davoudi employed both conventional and cutting-edge deep learning models to analyze the EEG data.
Precision at Its Best!
The results, published in May 2025 in NeuroImage, revealed that the new deep-learning model outperformed traditional machine learning. "With just a few minutes of EEG data, we could estimate an infant’s brain age with an accuracy of less than 30 days," Lippé reported. This is a remarkable tool for detecting both developmental delays and accelerations.
Brain Waves: The Key to Understanding Development
The research underscores the role of brain waves as indicators of brain maturity. For instance, alpha waves (6–9 Hz), linked to attention and relaxation, become more prominent as an infant develops, showcasing the brain's increasing capacity for cognitive integration. Conversely, delta waves (0.5–2.5 Hz), prevalent in infants and associated with deep sleep, gradually diminish as the brain matures.
Spotting Anomalies and Assessing Risks
Beyond merely estimating brain age, this non-invasive tool can identify anomalies in neurodevelopmental processes. In fact, infants with macrocephaly displayed noticeable delays in brain maturation compared to their peers. The study also established a correlation between brain age and behavioral, cognitive functions, assessed through adaptive behavior and information-processing tests.
A Glimpse into the Future of Pediatric Care
According to Lippé, these discoveries could revolutionize clinical practices. "Estimated brain age may enable us to identify children at risk of developmental disorders before behavioral signs manifest. It can also serve as a benchmark for monitoring therapeutic intervention effectiveness, offering a tangible measure of brain development progression," she stated.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)