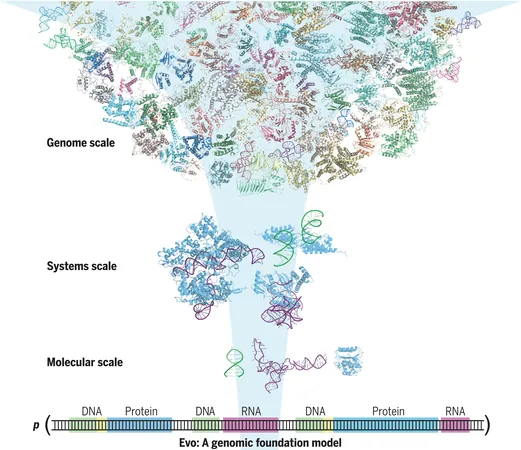
Revolutionary AI Model "Evo" Set to Transform Genetic Research and Design
2024-11-15
Author: Jacques
Introduction
In an exciting breakthrough for genetic research, a team of computer scientists, bioengineers, and artificial intelligence specialists from the Arc Institute and Stanford University has developed an innovative AI-based model called "Evo." This groundbreaking model is not just capable of decoding genetic sequences; it can also design new ones. Their research, published in the prestigious journal *Science*, outlines the development and potential applications of Evo, which may soon revolutionize medical research and disease treatment.
Implications of Evo
Christina Theodoris, affiliated with the Gladstone Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, described the implications of this work in a Perspective piece in the same journal issue. She emphasized that the development of Evo could have significant impacts on various fields, bringing us closer to new medical treatments and enhancing our understanding of genetic diseases.
The Evolution of AI in Genetics
The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT has opened new doors for artificial intelligence, extending their applications beyond mere text generation. This research harnesses the power of AI to analyze extensive DNA datasets, paving the way for innovative solutions in biological research. The Evo model was specifically trained on vast amounts of DNA data, equipping it to create new genetic sequences based on learned principles from existing data.
Training the Evo Model
Remarkably, the team trained Evo using an enormous dataset of 2.7 million microbial genomes, which included millions of gene sequences from bacteria known for targeting viruses. This process took four weeks and allowed Evo to gain insights into the functioning of DNA strands down to the nucleotide level, the foundational building blocks of life.
Initial Tests and Results
In initial tests, Evo was tasked with predicting the effects of specific mutations on proteins. When compared to established laboratory results, Evo's predictions were found to be highly accurate, demonstrating that it could perform tasks in minutes that previously took scientists years of intensive research and experimentation.
Future Potential
The researchers are optimistic about the future of Evo, suggesting that this model could significantly alter approaches to synthetic biology, making it more efficient and effective. With Evo, the possibilities are vast—ranging from the development of new biodegradable materials to advancing our understanding of genetic disorders.
Conclusion
As the field of synthetic biology evolves, experts anticipate that innovations like Evo will not only enhance our grasp of genetic engineering but also offer novel therapeutic avenues for some of the most pressing health challenges of our time. In summary, the advent of Evo marks a transformative moment in genetic research, one that holds the promise of reshaping science for years to come.






 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)