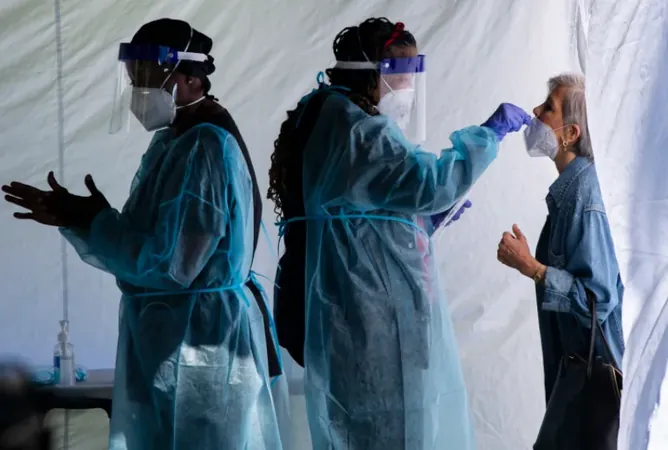
New COVID-19 Variant NB.1.8.1 Spreads Worldwide: What You Need to Know
2025-06-09
Author: Amelia
A newly identified COVID-19 variant, dubbed NB.1.8.1, is creating waves as it swiftly spreads across the globe, raising alarms among health officials. First detected in January 2025, this variant is part of the Omicron family and has already made its way to countries including the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, China, India, the Maldives, and Egypt.
Reports from Ireland indicate that NB.1.8.1 is presenting unique symptoms compared to previous strains. In addition to the familiar throat pain and fatigue, patients are experiencing troubling gastrointestinal issues like nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, heartburn, bloating, and abdominal discomfort.
Feeling under the weather? Irish health authorities caution anyone exhibiting these symptoms to stay home and limit contact with others until they recover. This strain can easily be confused with seasonal colds or stomach bugs, leading to potential outbreaks if precautions are not taken.
WHO Monitoring and Global Response
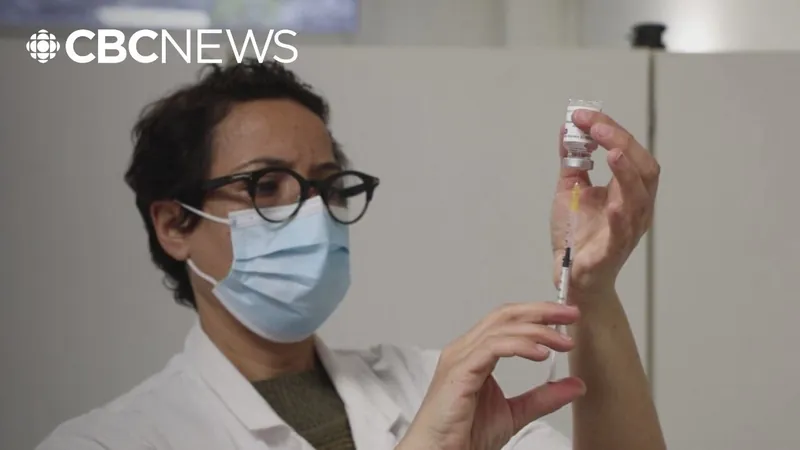
The World Health Organization has classified NB.1.8.1 as a ‘Variant Under Monitoring,’ highlighting its rapid spread while indicating it does not pose a significant immediate threat. According to the Global Virus Network, there’s currently no evidence to suggest that this variant causes more severe illness than its predecessors. Similar to earlier Omicron variants, NB.1.8.1 has genetic adaptations that enhance its transmissibility. However, vaccines—especially updated boosters—remain effective in shielding individuals from serious outcomes.
As breakthrough infections can still occur, particularly among unvaccinated individuals or those who haven’t had a recent booster, vaccinated persons are showing markedly lower rates of severe illness. Health experts emphasize that vaccination's primary advantage is not to prevent infection completely but to mitigate severe consequences like hospitalization, long-term complications, or even death.
Global Spread and Recent Data
Recent findings from the WHO reveal that NB.1.8.1 has been identified in at least 22 countries. Between late April and early May, its prevalence in global samples surged from a mere 2.5 percent to over 10 percent. In India, more than 4,300 active COVID-19 cases were reported by early June, with nearly 300 new cases in just one day. States like Delhi and Kerala have reported steady increases in infections.
In Taiwan, hospital visits for COVID-19 symptoms skyrocketed nearly 80 percent during the last week of April. In the United States, NB.1.8.1 has been found in several states, initially detected through airport screenings before moving into the community, affecting states like Washington, Ohio, and Hawaii. The U.S. continues to report approximately 300 COVID-related deaths weekly.
Vaccination Encouraged as Precaution
In light of this emerging variant, the Global Virus Network is urging everyone eligible to get vaccinated or receive booster shots. Adults over 65, individuals with chronic health issues, and pregnant women are particularly encouraged to ensure they are up-to-date with their COVID-19 vaccinations.
There’s also a strong emphasis on pediatric vaccination, especially for children who haven’t received an updated dose in the past year. Experts stress that vaccination during pregnancy delivers crucial protection for both mother and child, reducing the risk of hospitalization for infants and minimizing complications associated with COVID-19 during pregnancy.
A Call for Preparedness, Not Panic
While the rise of NB.1.8.1 has not led to any emergency measures, it serves as a stark reminder of the importance of robust global surveillance and cooperative scientific efforts. Experts assert that the emergence of new variants is anticipated, and we should approach them with preparedness rather than fear. This moment is not a crisis; it’s an opportunity to stay ahead in the ongoing fight against COVID-19.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)