
Nvidia’s GPUs Hit by Alarming Rowhammer Attack: What You Need to Know
2025-07-14
Author: Noah
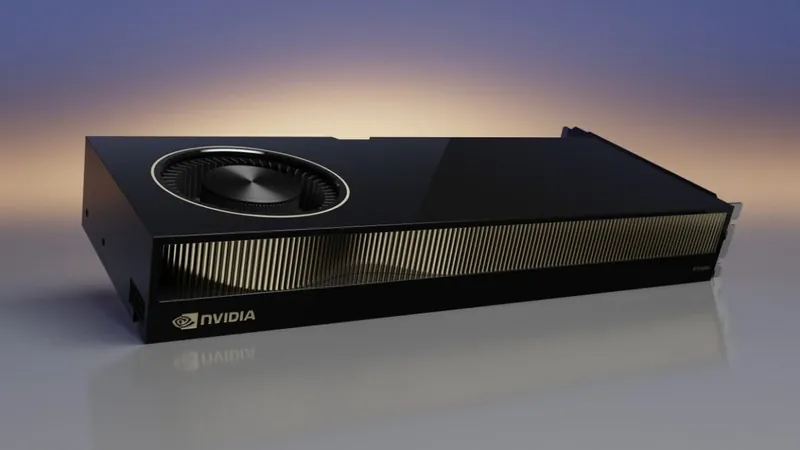
In a significant cybersecurity development, Nvidia has urged customers to take preventive measures against a newly uncovered vulnerability that exposes its RTX A6000 GPUs to Rowhammer bit-flip attacks. This recommendation comes with a stark warning: implementing these safeguards could reduce GPU performance by up to 10%.
Rowhammer attacks exploit physical weaknesses in DRAM chip modules, causing bits of data to flip unpredictably. Researchers recently demonstrated this tactic on Nvidia’s RTX A6000, a GPU crucial for high-performance computing, widely used across various cloud services. The discovery has far-reaching implications, posing severe risks to critical projects and applications.
The Mechanics of Rowhammer: A Recipe for Chaos
Essentially, Rowhammer allows attackers to manipulate memory data by rapidly accessing specific rows of memory cells, causing unintended changes nearby. Until now, such attacks were primarily directed at CPU memory chips, leaving the GPU sector relatively untouched—until now.
The research team unveiled 'GPUhammer,' marking the first successful Rowhammer assault on a discrete GPU. As GPUs evolve beyond mere graphics rendering into essential components of AI, machine learning, and high-performance computing, this vulnerability raises urgent concerns. Nvidia recently achieved a historic $4 trillion valuation, underscoring its dominance in this rapidly expanding field.
One Bit Flip Can Bring Models to Their Knees
The researchers’ proof-of-concept revealed a shocking consequence: a single flipped bit can drastically degrade the performance of deep neural networks, which are used in everything from autonomous vehicles to healthcare diagnostics. For example, a small tweak in data representation can plummet model accuracy from 80% to an alarming 0.1%—akin to instilling catastrophic brain damage in the algorithm! Imagine self-driving cars misinterpreting a stop sign as a speed limit sign, or medical models misdiagnosing patients.
Nvidia's Mitigation Strategy Comes with Performance Costs
To counteract this threat, Nvidia has advised users implement error-correcting code (ECC) systems that enhance memory integrity. However, these protective measures do come at a cost, potentially sacrificing up to 10% of performance—particularly impacting workloads on models like the 3D U-Net, significant for medical imaging.
Nvidia’s mitigation solution may not be foolproof. While ECC can correct single-bit errors, if multiple bits are disturbed in a single memory code word, it could create silent data corruption. Thus, users must tread carefully.
The Broader Impact: Vulnerability Across GPU Families?
Experts warn that other Nvidia GPUs might also be susceptible to Rowhammer-style attacks, particularly those from the Ampere generation using GDDR6 memory. Newer models, such as the H100 and the upcoming RTX 5090, boast built-in error detection mechanisms, potentially offering better protection. However, thorough testing against targeted Rowhammer maneuvers is still lacking.
A Game-Changer in Cybersecurity Risks
The emergence of GPUhammer marks a pivotal moment in cybersecurity, showcasing that even advanced GPU architectures, previously considered secure, are now in the crosshairs of sophisticated attacks. This revelation is expected to stir new conversations about data integrity and security protocols in both cloud and consumer environments.
As the situation develops, businesses and users reliant on Nvidia’s GPUs must adapt swiftly, ensuring they implement recommended defenses while remaining cautious about the performance trade-offs. The researchers behind this alarming discovery will reveal further insights at the upcoming 2025 Usenix Security Conference, making it a must-follow event for those in the tech and cybersecurity arenas.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)