
NASA's Webb Telescope Unveils Spectacular Stellar Jet on Milky Way's Edge
2025-09-10
Author: Michael
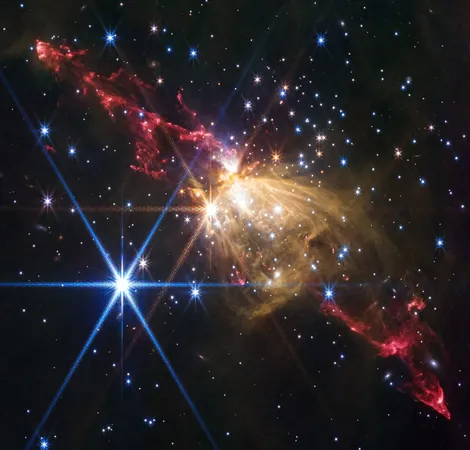
In an astonishing discovery, NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has captured a breathtaking image of a massive stellar jet erupting from a young, monster star. This extraordinary outflow stretches a staggering 8 light-years into space, approximately double the distance from our Sun to the nearest star system, Alpha Centauri.
Resembling a dramatic double-headed lightsaber from Star Wars, this stellar jet is rocketing through space at mind-blowing speeds of hundreds of thousands of miles per hour. Located in the breathtaking nebula Sharpless 2-284 (Sh2-284), the star at the center of this action weighs nearly ten times that of our Sun and sits a striking 15,000 light-years away.
The discovery was made almost by chance, as lead researcher Yu Cheng from the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan explained, "Before this observation, we had no idea that such a massive star with a powerful super-jet even existed in this region." Such incredible jets of molecular hydrogen from massive stars are rare across our galaxy.
These stellar jets represent a spectacular 'birth announcement' for new stars. Plasma is hurled from the star’s rotation axis, likely influenced by magnetic fields, highlighting the intricate processes involved in stellar formation.
While astronomers have documented many protostellar jets, most are linked to smaller stars. These unique jets offer critical insights into how new stars develop. Their structure, energy, and dynamics can tell us much about the physical characteristics of young stars.
Co-author Jonathan Tan from the University of Virginia expressed astonishment at the jet's symmetry and scale when they first observed it, stating, "The order and size of the jet truly surprised us." This finding indicates that protostellar jets must increase in scale corresponding to the star's mass.
In its striking infrared images, Webb has revealed a complex filamentary structure of the jet, demonstrating its interaction with interstellar dust and gas, forming distinct knots and shock waves.
The tips of the jet—which stretch far into space—reveal a timeline of the star's growth. Through the passage of time, it's evident that older material has traveled further from the star, showcasing a dynamic history.
Located on the fringes of our Milky Way, this distant star cluster is home to hundreds of stars that are still forming. Interestingly, these stars are in a low-metallicity environment, lacking heavier elements, which reflects conditions similar to those in the early universe.
Cheng emphasized the significance of this find, highlighting how such massive stars influence galactic evolution. He remarked, "Our discovery sheds light on the formation of massive stars in environments with low metallicity, essentially providing a glimpse into cosmic history."
The jets from these stellar giants encode stories of their formation processes. As Webb continues to unravel these mysteries, new insights about how massive stars are formed are emerging.
Astronomical debates surrounding massive star formation methods have persisted for over three decades. Some theories suggest that a chaotic process known as competitive accretion plays a key role, while others believe a more stable mechanism accompanies their growth.
Tan highlights that the spatial symmetry observed supports the core accretion theory, suggesting stable conditions during the star's formation.
Excitingly, there could be more massive stars lurking in the outskirts of our galaxy, possibly in earlier formation stages. Recent data from the Atacama Large Millimeter Array has hinted at another dense stellar core that may soon unveil its own jet.
This groundbreaking study has been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal, paving the way for further exploration.
The James Webb Space Telescope, functioning as the leading astronomical observatory, continues to unveil secrets of our universe, from our solar system to distant galaxies and beyond. This extraordinary mission, led by NASA alongside its partners, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), is charting an inspiring path towards cosmic understanding.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)