
NASA's Stunning Discovery: A Mysterious "White Spot" in the Sahara Desert
2025-08-22
Author: Michael
Astronauts Capture a Geological Marvel from Space
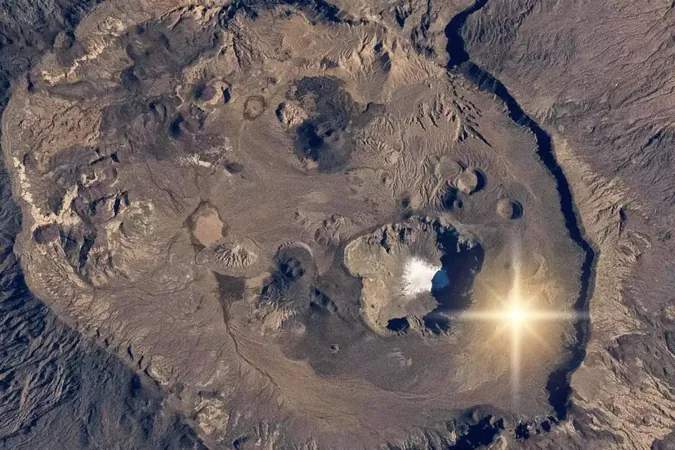
Astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) have unveiled a breathtaking sight: a striking white formation nestled within Africa’s largest desert. This eye-catching anomaly, perched atop an isolated volcanic peak in northern Chad, stands out vividly against the dark volcanic rocks surrounding it.
Unraveling the Secrets of Ancient Climate
The Emi Koussi stratovolcano, soaring over 3,400 meters above sea level, is one of the Sahara's highest peaks. Initially mistaken for snow due to its altitude, in-depth geological analysis revealed a captivating truth: these brilliant white deposits are not snow but salt remnants from an ancient lake that once filled the volcanic crater. This finding unearths a narrative of the Sahara’s dramatic climate evolution from lush greenery to today’s arid landscape.
Evidence of a Once-Watered Wonderland
Satellite images have uncovered clear signs of bygone water activity across the volcanic landscape, featuring dried riverbeds, erosion channels, and ancient canyons shaped by flowing water thousands of years ago. These geological markers provide solid evidence of the “Green Sahara” era—an age characterized by plentiful rainfall, rivers, and sprawling vegetation roughly 5,000 years ago.
Decoding Earth's Climatic History with Modern Technology
Thanks to advanced space exploration techniques, scientists can now reveal Earth’s forgotten environments from space. The ISS photography program, in collaboration with specialized partners, captures high-resolution imagery that ground-based studies simply cannot achieve. With the advancement of remote sensing capabilities, researchers are unveiling new layers of our planet's hidden history.
Key Discoveries and Their Implications
Researchers utilized various indicators to reconstruct the ancient Saharan landscape, including: - Mineral composition analysis pointing to evaporite formations - Erosional patterns reflecting sustained water flow - Sedimentary layers indicating lake level fluctuations - Fossils of aquatic organisms nearby - Chemical signatures suggesting a previously humid climate These discoveries expand our understanding of climate variability, highlighting how deserts like the Sahara are not static but dynamic environments shaped by complex geological and atmospheric changes.
A Reminder of Our Planet's Dynamic Past
The remarkable transformation of the Sahara from a lush landscape to a barren desert exemplifies the scale of natural climate change. This newfound knowledge sheds light on contemporary environmental research, showing that ancient climate records are preserved in unexpected places across the globe. As scientists continue to explore these geological time capsules, the white spot at Emi Koussi may hold the keys to understanding our planet’s past and its future climate trajectories.
Conclusion: The Multifaceted Value of Space Research
This discovery not only enhances paleoclimatology and geology but also provides vital insights for atmospheric science and future climate modeling efforts. It starkly demonstrates how orbital observations can yield transformative knowledge across multiple scientific domains.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)