
NASA's Cygnus Mission Hits a Major Snag: 11,000 Pounds of Supplies at Risk and Astronauts Left Stranded!
2025-09-23
Author: Liam
A Critical Mission Takes a Troubling Turn
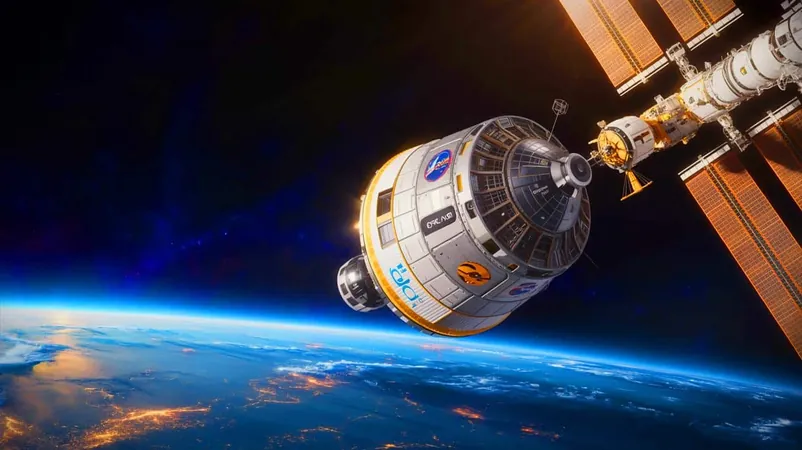
NASA's ambitions soared sky-high with the recent launch of Northrop Grumman's Cygnus XL spacecraft, set to deliver a staggering 11,000 pounds of vital supplies straight to the International Space Station (ISS). But disaster struck when the spacecraft's main engine unexpectedly shut down, leaving astronauts in a precarious situation and prompting urgent evaluations of alternative strategies.
Engine Failure: A Shocking Twist
The Cygnus XL's journey hit a critical roadblock when its main engine malfunctioned during crucial orbital adjustments meant to align with the ISS. Initially intended to make these adjustments seamlessly, the engine's abrupt failure has now delayed the arrival of life-sustaining supplies, originally scheduled for Wednesday. NASA's ground teams are scrambling to devise backup plans to facilitate contact with the ISS, albeit on a drastically revised timeline.
A Mission Millions Were Watching
Launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida, the Cygnus XL took off without a hitch, separating smoothly from its launch vehicle. The subsequent engine failure, however, casts a long shadow on the mission’s success. While NASA remains tight-lipped about the root cause of the engine troubles, they did assure the public that all other systems aboard Cygnus XL are functioning as intended.
Why This Mission Matters
This mission marks an impressive 22nd cargo resupply venture for Northrop Grumman, showcasing their integral support for the ISS. The Cygnus XL, boasting a 33% increase in cargo capacity, stands 5.2 feet longer than its predecessors, marking a significant leap in commercial space capabilities. It's loaded with fresh food, crucial hardware for ongoing scientific experiments, and essential spare parts—most notably components for the ISS's restroom facilities. The potential loss of these supplies isn't just a logistical nightmare; it poses serious threats to the astronauts’ day-to-day life in space.
Navigating Trouble: The Road Ahead
Cygnus' engine operates on a hypergolic propellant mix that's known for reliability, yet the current situation demands immediate contingencies. Engineers are exploring the possibility of using the spacecraft's smaller thrusters, originally meant for minor adjustments, to make larger orbital changes necessary for docking with the ISS. This workaround, however, carries risks as these thrusters weren't designed for such extensive maneuvers, raising questions about their effectiveness.
Future Missions in Jeopardy
The unforeseen complications of this mission spotlight the inherent risks of space travel. With Cygnus not designed for a return trip to Earth, timely docking with the ISS is critical. Failure to deliver could spell disaster for both cargo and vital scientific projects. Northrop Grumman's ability to navigate this crisis will influence both the current mission and future endeavors, as the demand for reliable space technologies continues to escalate.
Looking Forward: Lessons Learned
As NASA and Northrop Grumman race against time to find a solution for the cygnus mission, the spotlight turns to how space agencies can enhance reliability and safety in future missions. Each setback offers valuable lessons, underscoring the need for resilient systems that can withstand the pressures of space exploration.
With astronauts and Earth-bound teams holding their breath, the outcome of this mission could redefine operational standards for commercial space travel. Will engineering ingenuity save the day, or are we witnessing the tipping point in spacecraft reliability?







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)