
Lessons Learned from SpaceX's Latest Starship Flight: The Tile Conundrum!
2025-09-09
Author: William
In just two weeks following SpaceX's last monumental test flight of the Starship, engineers have uncovered crucial insights about its heat shield, pinpointed areas for improvement, and crafted a game plan for the next mission. This was unveiled by Bill Gerstenmaier, a high-ranking SpaceX executive, during his address at the American Astronautical Society's Glenn Space Technology Symposium in Cleveland.
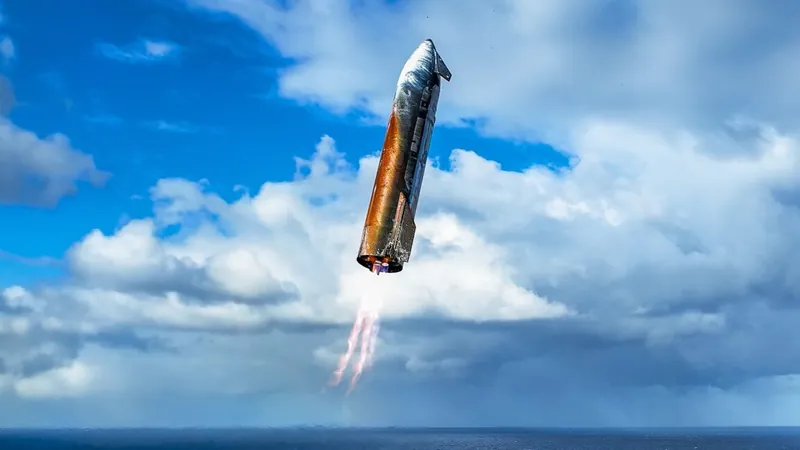
Lifting off from SpaceX’s Texas launch pad on August 26, this marked the groundbreaking 10th full-scale test of the colossal Super Heavy booster paired with the Starship upper stage. The stakes were high; SpaceX needed to address past propulsion failures and gather new data on the vehicle’s heat shield, made of thousands of specialized tiles designed to protect it during the harrowing reentry into Earth's atmosphere.
"The mission went exceptionally well," Gerstenmaier reported proudly. Just over an hour after launch, Starship achieved a controlled splashdown in the Indian Ocean, mere feet from its target, further showcasing the engineering prowess behind SpaceX's design.
However, upon inspecting the returning Starship, some distressing damage was evident—visible deterioration on the tail and flaps, along with a curious rusty orange coloration on the side of the 171-foot-tall rocket. This discoloration, according to SpaceX founding visionary Elon Musk, stemmed from experimenting with metallic heat shield tiles intended to assess their performance against traditional ceramic tiles.
Diving Deeper into the Technical Details
During the symposium, Gerstenmaier elaborated on the ambitious experiment with metallic tiles. "We essentially wanted to evaluate if non-ceramic tiles could suffice, opting for three metallic coverings due to their simpler manufacturing processes. Yet, the results were disappointing," he confessed. The metal tiles oxidized dramatically in the high-oxygen environment of reentry, leading to the unexpected orange hue.
The pursuit of a robust heat shield is pivotal, especially if Musk's vision of rapid reusability—turning around Starships within just 24 hours—is ever to be realized. Previous NASA missions employed fragile ceramic tiles that required constant maintenance, whereas SpaceX aims to leverage the higher melting point of stainless steel for greater durability.
Notably, the symbiotic relationship between the tiles and the underlying material revealed alarming vulnerabilities. Observation of white patches indicated heat penetrating the gaps between the tiles, compromising the protective layer beneath.
Innovative Solutions on the Horizon
But hope is on the horizon! SpaceX is exploring a new solution dubbed "crunch wrap"—a novel material designed to seal gaps between the tiles. Gerstenmaier explained that this could facilitate a better fit than the traditional gap fillers, which have been prone to dislodging during flight.
The next test flight, Flight 11, slated for October, will utilize this exciting new method. The focus will shift towards maximizing performance and reliability, as SpaceX prepares to unveil their upgraded V3 starship and booster in the coming year.
Looking Ahead: A New Era for Starship Missions
What’s on the horizon? Gerstenmaier revealed ambitious plans for future missions, including potential orbital flights by mid-2024, crucial for the deployment of next-gen satellites and preparation for missions to the Moon and Mars. New developments in propellant transfer technology are also in the pipeline.
As SpaceX continues to break boundaries, the insights from this flight embody the rapid iterative culture that sets the company apart. Each test not only reshapes the Starship but also enhances the velocity at which we explore our universe.
With stakes this high, the journey from suborbital tests to ambitious orbital missions is one to watch closely! SpaceX's relentless pursuit of innovation may soon change the face of space travel forever.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)