Groundbreaking Research Reveals Shocking Truth About Ancient Sea Level Rise!
2025-03-24
Author: Sophie
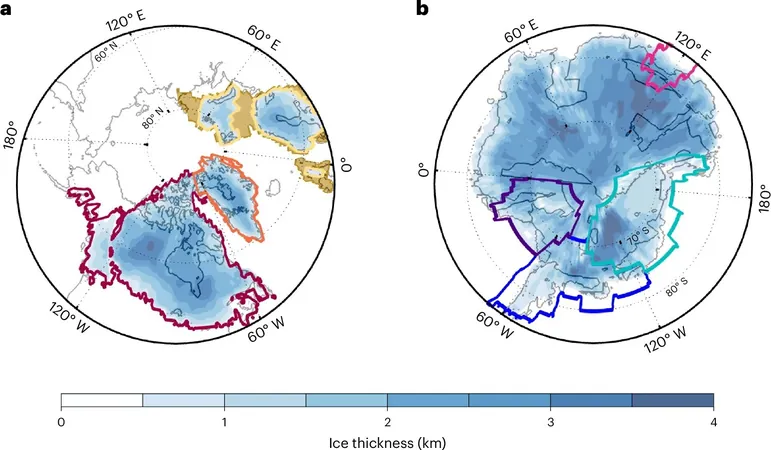
Around 14,500 years ago, as the last ice age drew to a close, our planet experienced a cataclysmic event that sent sea levels skyrocketing by up to 65 feet in a mere 500 years. This sudden rise, known as Meltwater Pulse 1a, has puzzled scientists for decades, leaving them to wonder which massive ice sheets were responsible for releasing such an incredible volume of water.
In a game-changing study recently published in Nature Geoscience, researchers from Brown University have unveiled an updated physical model that sheds new light on this dramatic phenomenon. Their findings reveal a complex interplay of ice sheet dynamics, potentially altering our understanding of global sea level rise today.
What Triggered the Meltdown?
The research team discovered that an initial melting in North America's Laurentide ice sheet acted as a catalyst for a catastrophic chain reaction. This modest beginning led to widespread ice loss across Europe, Asia, and Antarctica. Lead researcher Allie Coonin, a Ph.D. candidate at Brown's Department of Earth, Environmental and Planetary Sciences, emphasized, “Our study shows distinct melting patterns across hemispheres, indicating mechanisms connecting these ice sheets globally, which is critical for evaluating the stability of Greenland and West Antarctic ice sheets in the current climate crisis.”
Unraveling the Mystery of Sea Level Change
To decode the events of Meltwater Pulse 1a, scientists examine preserved sea level records found in ancient shorelines and ocean sediments, laden with fossilized corals and other remnants that provide clues to past sea levels. By utilizing a method called sea level fingerprinting, they trace the origins of the meltwater. Notably, melting ice sheets don't simply raise sea levels uniformly; local geography and gravitational forces mean some areas experience greater increases, while others might face declines.
This dynamic is influenced by factors such as gravity's pull from ice sheets and how Earth's crust reacts to the melting ice. As ice melts, the land beneath it rebounds, but this crustal deformation redistributes ocean water, impacting global sea levels in unexpected ways.
Innovations in Modeling Sea Level Dynamics
Previous research primarily focused on elastic deformation—the immediate reaction of the Earth's crust to changes—but Brown University's study introduced a new perspective by integrating viscous deformation, where the Earth's mantle behaves like a thick fluid. Historically, viscous responses were thought to unfold over millennia, but fresh insights suggest they can manifest in decades to centuries, making them significant for short-term events like Meltwater Pulse 1a.
A Paradigm Shift in Understanding Past Climate Events
The researchers propose a revised scenario whereby the event began primarily with the melting of the Laurentide ice sheet, which alone contributed about 10 feet to rising sea levels. This was soon followed by substantial contributions from Eurasia and the West Antarctic ice sheets, which added 23 feet and 15 feet respectively. This contrasts sharply with earlier models that attributed the event to either North American or Antarctic sources without considering interhemispheric links.
Coonin asserts, “Our findings underscore the importance of precise physics in predicting sea levels, showing that a comprehensive understanding can redefine our predictions.”
Implications for Today’s Climate
While unraveling the complexities of past sea level events is vital, researchers caution that more investigation is necessary to fully comprehend the interconnectedness of various ice sheets. The implications are profound and timely, especially given that the current rapid melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet may be influencing the stability of the Antarctic Ice Sheet, even as they exist on opposite ends of the globe.
Could the shocking revelations from our planet's past hold crucial lessons for the challenges we face today? As scientists delve deeper into this icy mystery, the stakes couldn’t be higher for understanding our planet's future!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)