
Groundbreaking Discovery: Mars' Inner Core Finally Revealed!
2025-09-04
Author: Noah
The First Solid Core Beneath the Red Planet!
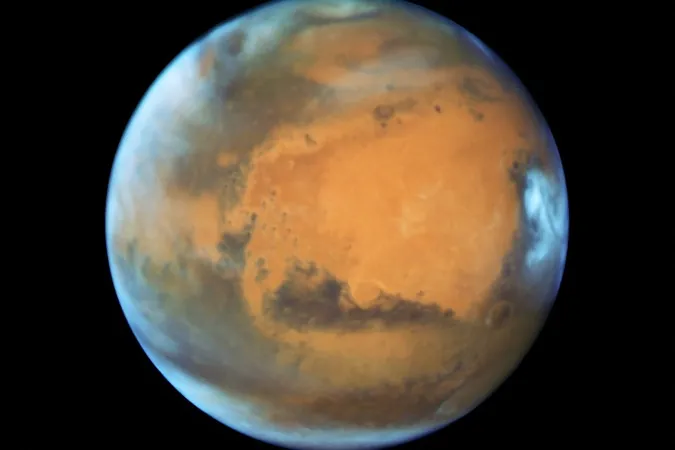
In an incredible breakthrough that has sent shockwaves through the scientific community, researchers from China and around the globe have unveiled the existence of a solid inner core on Mars, measuring approximately 600 kilometers in radius. This pivotal discovery offers vital insights into the evolution of Mars' magnetic field and deepens our understanding of the Red Planet's history.
Mars: The Earthly Twin of Our Solar System
Often regarded as the most Earth-like planet in our solar system, Mars has long been a focal point in the quest to understand planetary structure and evolution. From its captivating landscapes to its tantalizing potential for life, Mars remains a primary target for deep space exploration. However, probing its internal structure has proved to be a daunting challenge.
Unlocking Mars' Secrets: A Historic Challenge
While Earth's inner core was theorized in 1936 through seismic waves, confirming its solid nature took decades. Investigating Mars, with its weak signals and interference from noise, presents even greater difficulties. Despite recording thousands of marsquakes, extracting meaningful data about the planet's deep interior has been a substantial hurdle.
A Collaborative Effort with Revolutionary Techniques
Leading the charge are researchers Sun Daoyuan and Mao Zhu from the University of Science and Technology of China, who, in collaboration with international experts, utilized data from NASA's InSight lander. By applying innovative array analysis techniques to 23 carefully chosen marsquakes, they successfully tapped into the seismic waves that traverse Mars’ core.
Mars: A Layered Interior Structure!
Their findings, published in the prestigious journal Nature, confirm that Mars possesses a layered core structure. The outer core is liquid, while beneath it lies a solid inner core with higher seismic wave speeds. Remarkably, this inner core constitutes about one-fifth of the planet’s total radius.
Significant Differences: Insights into Composition
Data analysis revealed a 30% increase in wave velocity and a 7% density disparity between Mars' outer and inner cores. This led to a further exploration of the inner core’s mineral makeup, revealing it comprises not only iron and nickel but also contains 12-16% sulfur, 6.7-9% oxygen, and a maximum of 3.8% carbon. Such a composition sheds light on the planet’s magnetic field evolution from its vibrant beginnings to its current dormant state.
A Boon for Future Space Missions!
This study marks a historic first, establishing a solid inner core in a planet beyond Earth and confirming that Mars shares a core-mantle differentiation akin to our own planet. The groundbreaking methodology developed here opens up thrilling possibilities for future missions, such as lunar explorations, enhancing our capability to investigate the internal structures of other celestial bodies.
Community Praise for Pioneering Research
The quality of the research has drawn applause from the scientific community. A reviewer thanked the authors for their meticulous approach in tackling the challenges of Martian seismology, highlighting the stout nature of their findings.
This extraordinary discovery not only enhances our grasp of Mars but also ignites excitement for the ongoing saga of space exploration, opening doors to unravel more planetary mysteries.







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)