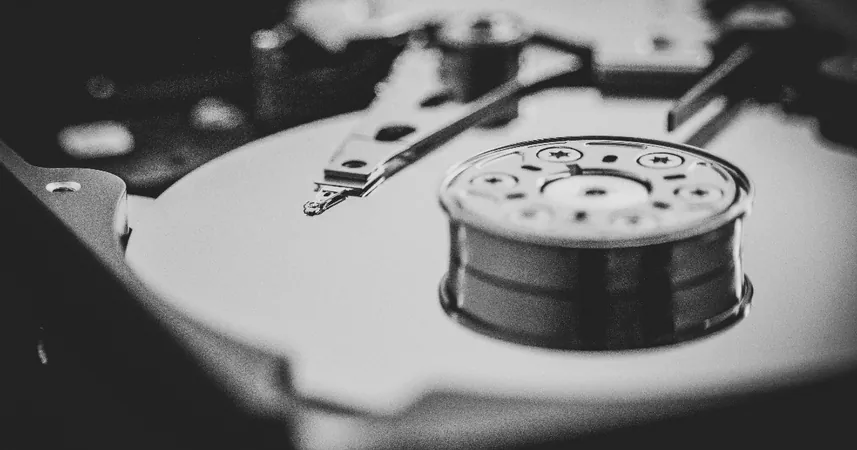

Google Cloud's Game-Changing HDD Tier for Spanner Database: Slash Costs by 80% Now!
2025-03-22
Author: Liam
Introduction
In a groundbreaking move, Google has unveiled a new tiered storage option for its popular Spanner database on Google Cloud. This innovative HDD (Hard Disk Drive) tier is set to transform how businesses manage their data by offering storage costs that are a staggering 80% less than the traditional SSD (Solid State Drive) option. This cost-effective shift focuses on optimizing older data while eliminating the headaches associated with conventional data migration.
The HDD Tier vs. SSD Tier
While Google's default SSD tier is tailored for high-performance data needs requiring rapid access and low latency, the newly introduced HDD tier caters to larger datasets that are accessed infrequently or do not require immediate retrieval. This tiered storage strategy is managed by automated background processes that intelligently move data from SSD to HDD based on user-defined policies, ensuring seamless access across both storage options.
The Importance of Data Storage Evolution
The Google Cloud team emphasizes a key insight: as time passes, the operational importance of many database records diminishes, while their role for reporting and compliance becomes more prominent. This evolution means that “cold” data— data no longer actively used—can be stored more economically without compromising the accessibility of vital “hot” transactional data. Consequently, businesses are now incentivized to seek out more cost-effective solutions for archiving historical information.
Challenges with Traditional Storage Methods
Matthew Muckloo, a software engineer at Google, and Piyush Mathur, group product manager, highlight the challenges associated with traditional storage methods. They note that shifting to alternative storage types typically involves complex data management pipelines, often leading to performance degradation. Manual segregation of data across storage solutions can also complicate data retrieval and raise governance issues requiring extensive audits.
New Storage Tiering Capabilities
However, with the new storage tiering capabilities rolled out in Spanner, organizations can apply these strategies at various levels—be it database, table, column, or secondary index—allowing for nuanced control over data storage. For instance, datasets like JSON product attributes that are rarely accessed can be transitioned to HDD without necessitating table restructuring. Simultaneously, indexes can remain on the faster SSD, optimizing performance while reducing costs.
Activating Tiered Storage
To activate tiered storage, users must establish a locality group specifying the desired storage options (SSD as default or HDD). This setup includes parameters such as the “ssd_to_hdd_spill_timespan,” which dictates how long data will stay on SSD before being transitioned to HDD. For example, executing the command: CREATE LOCALITY GROUP recent_on_ssd OPTIONS (storage = 'ssd', ssd_to_hdd_spill_timespan = '15d'); This will enforce a spill policy transitioning data to HDD after a designated period, with a minimum retention period of just one hour on SSD.
Competitors' Offerings
While Google Spanner is leading the charge in tiered storage solutions, it’s worth mentioning that competitors like Amazon's DynamoDB also offer similar capabilities under the hood, providing Standard and Standard-IA storage classes that come with varying costs for storage and data retrieval.
Conclusion
In a world of rising data costs, Google's introduction of the HDD tier for Spanner is a game-changer—empowering businesses to cut expenses while efficiently managing their data. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to revolutionize your data storage strategy!








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)