Dengue's Global Impact: Shocking Findings on Disability and Age Variations
2025-06-09
Author: Jacques
Dengue: A Rising Global Health Threat
Dengue fever is rapidly emerging as a significant global health crisis, characterized by a wide array of clinical manifestations that differ drastically across age groups and geographic regions. This compelling study aims to uncover the global disability weights (DWs) associated with dengue, utilizing data from various clinical manifestations to better inform public health strategies and interventions.
Research Methodology: A Comprehensive Data Dive
Our robust investigation involved an extensive search through six major databases, including renowned platforms like Scopus and PubMed, for studies on dengue's clinical manifestations up to December 2023. The research utilized Monte Carlo simulations to estimate DWs by analyzing frequencies of clinical manifestations alongside values from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study.
Key Findings: Differences Between Adults and Children
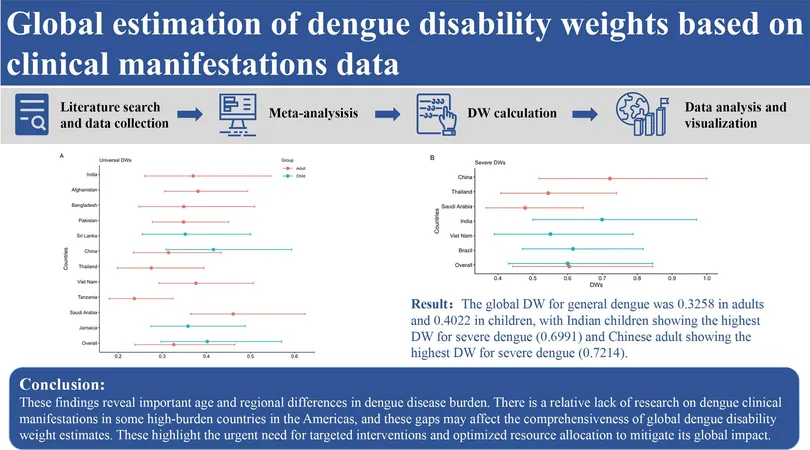
In a captivating analysis covering 35 studies involving 7,109 adult cases and 17 studies with 2,996 pediatric cases, striking discrepancies emerged. Adults suffered from significantly higher rates of muscle pain and fatigue, while children experienced a worrisome prevalence of severe dengue. The global DW was calculated at 0.3258 for adults and an alarming 0.4022 for children, suggesting that dengue poses a greater threat to younger populations.
Geographical Insights: A Closer Look at Dengue's Burden
Predominantly sourced from South and Southeast Asia, with India leading the charge in dengue-related research, this investigation revealed that this region harbors the highest dengue burden. In 2021 alone, India suffered approximately 352,468.54 person-years lost to this disease.
The Alarming Rise of Dengue Cases
With a staggering 7.6 million dengue cases worldwide reported by the WHO as of April 2024, alarm bells are ringing. The Americas have experienced a surge, with Brazil accounting for over 80% of cases, necessitating urgent and effective public health interventions.
The Call to Action: What Needs to Change
This study starkly highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions, especially in high-burden areas and among vulnerable populations. As severe dengue continues to pose a critical health threat, optimizing resource allocation and improving health care quality are essential for controlling its spread.
Urgent Need for Further Research
Despite these important findings, a glaring lack of research persists in high-burden regions like the Americas. Addressing these gaps is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of global dengue disability weights and the effective implementation of health strategies moving forward.
Conclusion: A Clear Call for Global Action
Dengue's increasing incidence, especially among children, underscores the importance of age-specific management strategies and resource allocation. This study serves as a wake-up call for policymakers to prioritize dengue response and prevention measures, especially in regions most affected.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)