
Astronomers Unveil 'Fossil Galaxy' Frozen in Cosmic Time: A Look Back at the Universe's Ancient Origins!
2025-06-30
Author: Michael
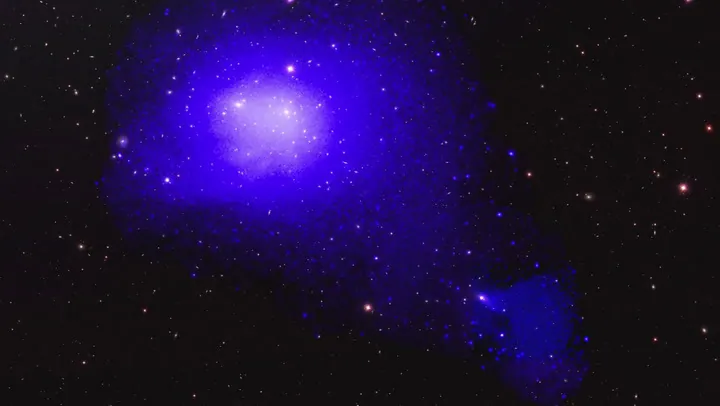
In an astounding discovery, astronomers have found a distant galaxy that serves as a "cosmic fossil," having remained "frozen in time" for an incredible 7 billion years!
Similar to how dinosaur fossils illuminate the history of life on Earth, the galaxy KiDS J0842+0059 could unlock secrets about the early universe and its evolution. This remarkable find is pivotal for understanding the conditions under which ancient galaxies formed.
What Makes a Cosmic Fossil?
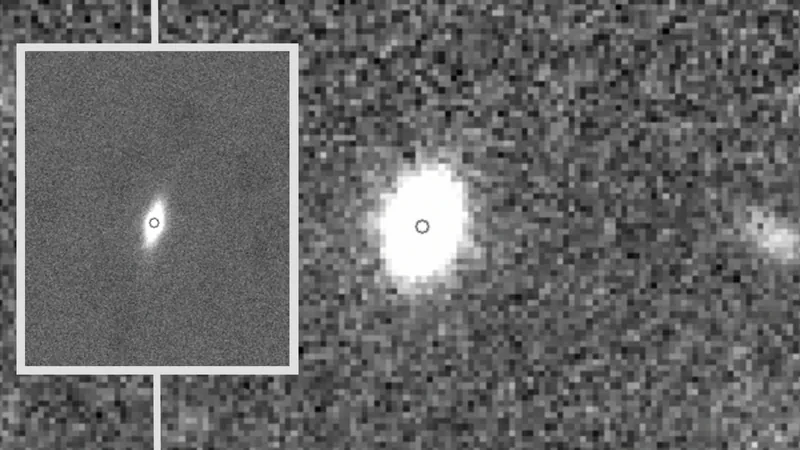
A cosmic fossil is a galaxy that has evaded the chaos of collisions and interactions with others, acting like a pristine time capsule. Research conducted using data from the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT) confirms that KiDS J0842+0059 has exhibited astonishing stability, remaining unchanged while the universe evolved around it.
Key Insights from the Discovery
Crescenzo Dove, co-leader of the research team and a scientist at the National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), remarked, "We have discovered a galaxy that has been 'perfectly preserved' for billions of years—an archaeological find that reveals how the first galaxies came into existence!" He likened fossil galaxies to the dinosaurs of the universe, emphasizing that studying them helps astronomers uncover the environments that fostered their formation.
The Discovery Journey of KiDS J0842+0059
Located a staggering 3 billion light-years from Earth, this galaxy was initially discovered in 2018 by the KiDS (Kilo Degree Survey). Groundbreaking imaging from the Very Large Telescope Survey Telescope (VST) enabled astronomers to analyze its size and mass. Further measurements from the Very Large Telescope (VLT) indicated that KiDS J0842+0059 harbors a stellar mass approximately 100 billion times that of our Sun, yet is more compact than similar galaxies. Notably, it has experienced little to no star formation throughout its existence, reinforcing its identity as a cosmic fossil.
Peering Deeper with LBT Technology
To clarify uncertainties regarding the galaxy's characteristics, the research team employed the adaptive optics system of the LBT to capture sharper, high-resolution images—ten times clearer than those previously available. Chiara Spiniello, a researcher at the University of Oxford, stated, "We have confirmed that KiDS J0842+0059 is indeed compact and a true galaxy relic, resembling NGC 1277, a similar stunted galaxy much closer to our own.
Revolutionizing Our Understanding of Galaxies
Discoveries like KiDS J0842+0059 and NGC 1277 suggest that certain galaxies can form rapidly, remain compact, and dodge cataclysmic interactions for billions of years. Understanding these cosmic fossils could help reconstruct the early formation history of today's massive galaxies, which unlike relics, have grown through fusion processes and matter accretion.
Excitingly, with advanced technologies like adaptive optics and the capabilities of the LBT, astronomers are poised to expand their search for and study of new relic galaxies. The forthcoming Euclid space telescope promises to offer unparalleled quality and high-resolution data, propelling our understanding of the universe to new heights.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)