
World Diabetes Day: Unveiling the 6 Serious Complications Linked to Gestational Diabetes
2024-11-14
Author: Ming
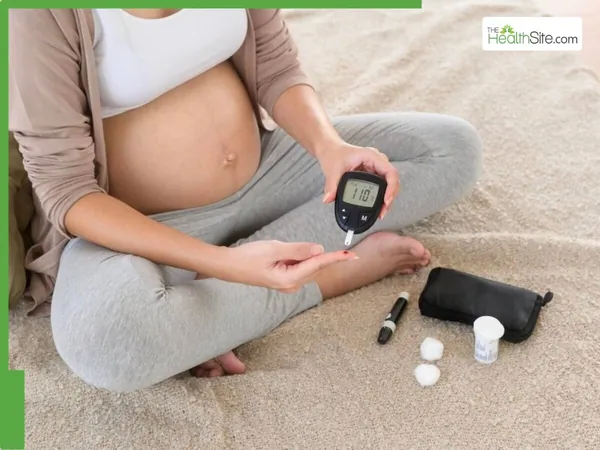
Gestational diabetes, characterized by insulin resistance during pregnancy, poses significant health risks for both the mother and her unborn child. When a woman's body struggles to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands during pregnancy, it results in elevated blood sugar levels. Managing gestational diabetes requires critical lifestyle changes, including dietary adjustments, regular exercise, and sometimes medication to safeguard a healthy pregnancy.
Understanding the intricacies of gestational diabetes is crucial, as it can have dire implications for a mother's health and her baby's wellbeing. Elevated blood sugar levels can adversely affect pregnancy outcomes, making awareness and preventive measures vital.
What Triggers Gestational Diabetes?
Several factors may increase a woman's risk of developing gestational diabetes: - Being overweight or obese - A family history of diabetes - A prior pregnancy with gestational diabetes - Hormonal imbalances such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) - Sedentary lifestyles According to Dr. Tanveer Aujla, a senior consultant obstetrician and gynecologist at Motherhood Hospitals in Noida, understanding these risk factors is essential for intervention and management, as gestational diabetes can lead to significant complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
Six Serious Complications of Gestational Diabetes
Here are six grave complications associated with gestational diabetes that expectant mothers should be aware of:
1. Preeclampsia
This pregnancy-associated condition results in hypertension and can manifest through symptoms such as swelling, fatigue, and protein in urine. If left unmonitored, preeclampsia can cause organ damage and compromise blood flow to the placenta. Regular check-ups are crucial for early detection and management.
2. Preterm Birth
Women with gestational diabetes face a heightened risk of preterm labor and delivery. Babies born prematurely are prone to numerous health challenges, including difficulty maintaining body temperature, developmental delays, and respiratory problems. Effective blood sugar management can help mitigate this risk.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)