Will Tuberculosis Among Students in Shanghai Surge? A Bold Prediction Using Markov Modeling!
2025-08-12
Author: Rajesh
The Growing Concern: Tuberculosis in Shanghai's Student Population
In Shanghai, students form a crucial demographic when it comes to combating tuberculosis (TB). A predictive study utilizing a dynamic Markov model aims to forecast the future trends of active tuberculosis (ATB) among these students, projecting serious implications through 2035 if strategic interventions are not undertaken.
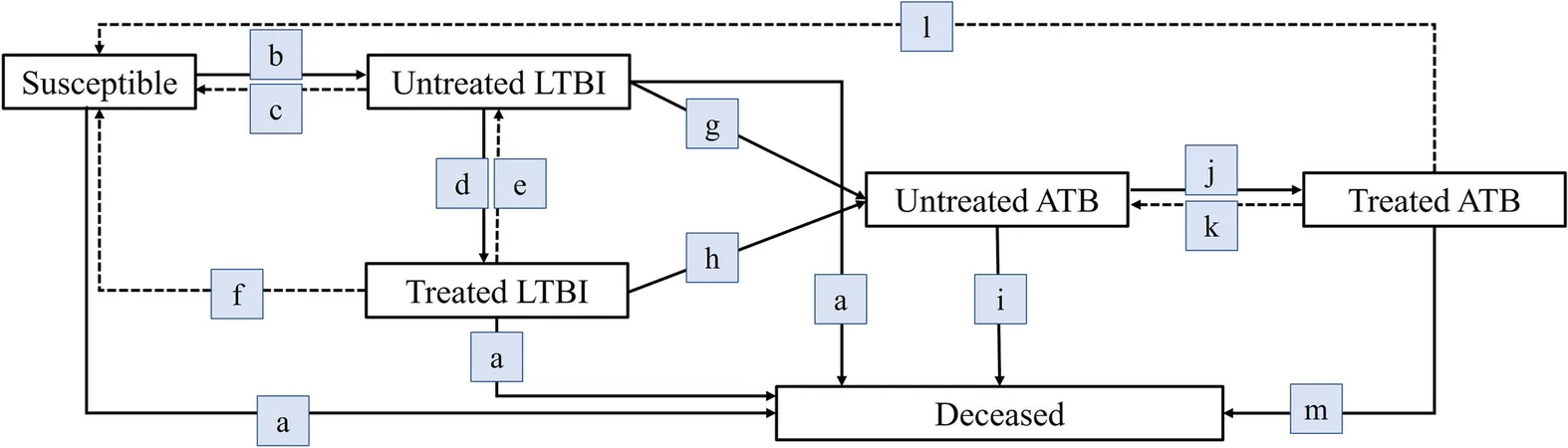
How the Study Works: The Innovative Markov Model
The study harnesses the power of a Markov model—tracking six distinct states of TB transmission—in a simulated cohort of 100,000 individuals. It evaluates the prevalence of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) and ATB, split by those who undergo the necessary treatments.
Startling Findings: What the Numbers Reveal
Currently, under existing control measures boasting no additional interventions, ATB prevalence is expected to see only a slight dip, from a concerning 14.80 per 100,000 by 2035. Expanding tuberculosis preventive treatment (TPT) coverage—set at varying percentages of 20%, 50%, and 80%—offers only modest reductions in prevalence. But here's the kicker: if detection rates of LTBI increase to 35%, the impact escalates drastically, slashing ATB prevalence by up to 80.46%! This paints a stark reality—current strategies are insufficient.
The Call to Action: Need for Enhanced Strategies
To effectively address the TB epidemic, a proactive approach is necessary. With the World Health Organization's (WHO) ambitious goals—aiming for a dramatic 90% decrease in incidence and a 95% drop in mortality by 2035—the time to act is now. Current TB control measures, especially in school settings, need an upgrade, as the presence of even a single infectious TB patient can incite an outbreak that spirals out of control.
Barrier to Progress: Low Acceptance Rates of Treatment
Disturbingly, data suggests that TPT acceptance rates among students with LTBI in Shanghai are dismally low. Past reports reveal that not a single student contact with LTBI received TPT during multiple outbreaks in 2019. This represents a colossal gap in the strategy to curb TB.
A Solution in Sight? Key Recommendations and Implementation
To expand TPT accessibility, pivotal strategies must be executed. This includes identifying LTBI infections proactively, bolstering diagnostic capabilities, and ensuring effective communication around treatment benefits. Engaging stakeholders, enhancing funding mechanisms, and educating healthcare personnel about LTBI could forge a pathway to a healthier future for Shanghai's youth.
Conclusion: The Stakes Are High!
As this study reveals, the future burden of ATB among students in Shanghai hangs in the balance. Without urgent action to enhance both detection rates and TPT coverage, the city risks falling into a deepening TB crisis—one that modern medicine once thought was under control. The fight against TB isn’t over; it’s just the beginning.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)