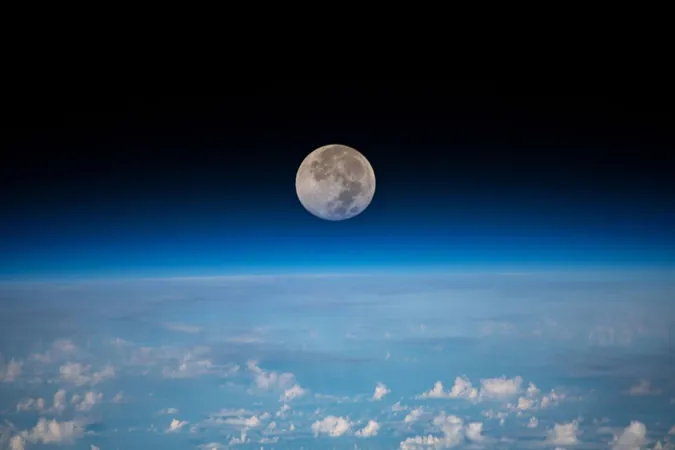

Urgent Warning: Cislunar Space Debris Threatens Future Lunar Missions!
2024-09-27
Author: Nur
A Growing Concern Over Space Junk Between Earth and the Moon
In a startling revelation, researchers from Purdue University have raised alarms about the rising quantity of space debris in cislunar space—the region between Earth and the moon. This increasing volume of artificial objects can have catastrophic implications for future lunar exploration missions, making it imperative to develop robust tools for debris characterization and management.
Understanding the Risks of Cislunar Debris
The researchers, Arly Black and Carolin Frueh, flagged a crucial lack of space domain awareness as cislunar activities ramp up. Historical data highlights that most of Earth’s orbital debris stems from collisions, explosions of propellant tanks, battery detonations, and the natural degradation of aging spacecraft. Their investigations revealed that fragmentation events could eject debris far beyond its orbital confines, with some fragments potentially returning to Earth.
Unlike Earth, where even small atmospheric drag helps to clean up space debris, cislunar space lacks such natural mechanisms. Objects in orbit around the moon remain trapped due to lunar gravity, which raises pressing concerns about the long-term sustainability of lunar operations.
Increased Lunar Activity Calls for Immediate Action
The urgency of this situation is underscored by the surge in international lunar missions. Various space agencies, including NASA, China, India, and Israel, are actively engaged in lunar exploration. Notable missions include the Indian Chandrayaan-3 mission, NASA’s CAPSTONE operation, and China's ambitious lunar landers and rovers. These missions are crucial for scientific advancements, but they also heighten the risk of space debris accumulation.
NASA's Artemis program is also set to amplify lunar traffic with its plans for the Gateway outpost, aimed at supporting lunar missions and eventually enabling a return to the moon's surface. The researchers warn that as this activity intensifies, so does the risk of spacecraft collisions and subsequent debris incidents.
The Chaotic Dynamics of Cislunar Space
Researchers Black and Frueh have pinpointed that while some models exist to predict spacecraft breakup in specific cislunar orbits, comprehensive global modeling is still in its infancy. Solar radiation pressure and gravitational influences from celestial bodies like Jupiter further complicate debris dynamics. They assert that understanding these interactions is essential to mitigate risks in cislunar space.
"This complex environment poses unique challenges," Black said. "Cislunar space dynamics are far from straightforward, and consequences of fragmentation can ripple through both the Earth-moon system and beyond."
The Inevitable Challenge of Fragmentation
According to Frueh, the fragmentation of human-made objects in this region is not a matter of "if," but "when". The consequences can be severe, with debris potentially impacting lunar missions, Earth-orbiting satellites, or even re-entering the atmosphere. One historical case of concern involved the Snoopy module from Apollo 10, which was eventually found crossing Earth’s path after being expelled into solar orbit.
Both researchers assert that a proactive approach is necessary to analyze cislunar debris before catastrophic events occur. "Understanding these dynamics will help us develop potential mitigation strategies," Frueh emphasized, urging the global community to recognize the escalating dangers in a rapidly evolving space environment.
Concluding Thoughts: The Call for Action
The implications of their findings indicate a critical need for enhanced monitoring and analysis of cislunar debris to ensure the safety and sustainability of future lunar exploration endeavors. As various nations forge ahead with ambitious lunar projects, the potential dangers of space debris could become an imminent threat, making swift action essential to safeguard the future of humanity’s endeavors in space.
Stay tuned as we explore how advancements in technology might provide solutions to these pressing concerns!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)