Urgent Health Screening Reveals Alarming Infectious Disease Rates Among Migrants in Italy!
2025-08-28
Author: Wei Ling
The Rise of Migration: A Decade of Change
Over the last ten years, global migration has surged dramatically, particularly in Europe and Asia. In Europe, the international migrant population skyrocketed nearly 16%, jumping from about 75 million in 2010 to an astonishing 87 million by 2020.
Italy's Migration Surge: The 'Refugee Crisis' Explained
Italy's migration dynamics have been tumultuous, particularly during the so-called refugee crisis from 2014 to 2017. The peak occurred in 2016, with a staggering 181,436 sea arrivals. Recent years have seen fluctuations, with over 100,000 new arrivals noted in both 2022 and 2023, largely from North and Central Africa, and increasing numbers from Asian nations like Bangladesh and Pakistan.
The Critical Health Impact of Migration
Migration doesn't just involve people; it brings significant health challenges. The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) has emphasized the need for rigorous health screening for newly arrived migrants, recommending checks for tuberculosis (TB), HIV, hepatitis B and C, schistosomiasis, and strongyloidiasis among others. Early detection is vital for both individual well-being and public health.
Infectious Diseases: The Hidden Dangers
Many infectious diseases prevalent among migrants can lead to severe, long-lasting health issues if left untreated. Diseases like TB and viral hepatitis pose serious transmission risks, while conditions such as schistosomiasis can have debilitating effects, including complications affecting vital organs.
Crucial Screening Efforts in Verona
A significant study conducted in Verona province evaluated the health of recently arrived migrants by assessing the prevalence of various infectious diseases between April 2014 and June 2015. The findings underscored the necessity of including helminthic infections in routine screening protocols for better health outcomes.
Diving Deeper: The Data Revealed
This current study aims to analyze a broader cohort of asylum seekers and undocumented migrants in Italy, focusing on their health to refine existing screening strategies. A considerable number of participants were screened, revealing alarming rates of infections.
Shocking Statistics: Migrant Health Screenings
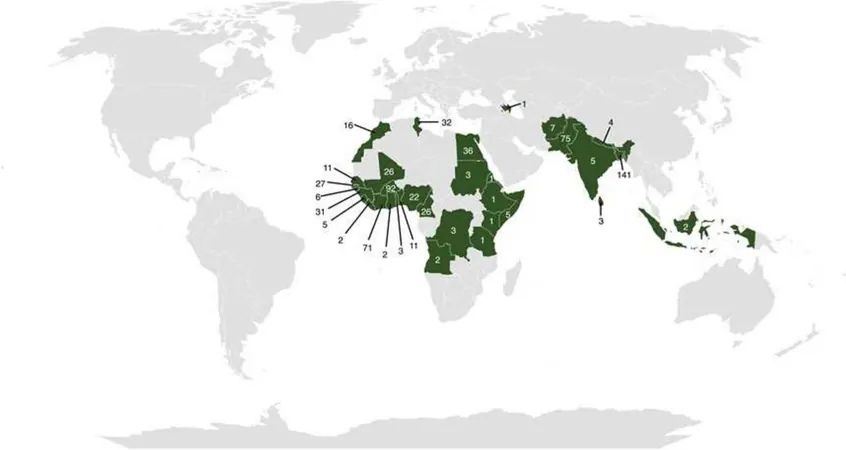
Out of 674 migrants screened, predominantly male with a median age of 25, a clear geographic trend emerged: 52.2% hailed from sub-Saharan Africa, 35.3% from Asia, and 12.5% from North Africa. Health screenings unveiled shocking findings: 1. **HIV:** 10 out of 672 tested positive (1.5%), predominantly from sub-Saharan Africa. 2. **Hepatitis B:** 6.1% tested positive for chronic infection, with a high percentage of the cohort eligible for vaccination. 3. **Tuberculosis:** 24.5% of migrants tested positive for TB infection, with 1.2% diagnosed with TB disease!
The Hidden Threat of Helminthic Infections
Surprisingly, helminthic infections are rampant. Around 12.3% were found to have at least one helminth present, with the prevalence of schistosomiasis at an eye-opening 12.9% exclusively among migrants from sub-Saharan Africa. The alarming rates underscore the urgency for targeted screening.
Eosinophilia: A Warning Sign
Eosinophilia, an important indicator of helminth infections, was detected in nearly 18.3% of the migrants screened. The data indicated that a significant majority of those with eosinophilia were linked to schistosomiasis and strongyloidiasis, reinforcing the need for comprehensive health evaluations.
Conclusions: A Call to Action!
The findings from this extensive study highlight an urgent need for systematic health screening protocols for migrants arriving in Italy and Europe. With significant differences observed in infectious disease prevalence based on geographical origin, there is a pressing necessity to adapt and enhance current health policies in response to the evolving migration landscape. Failure to act could have serious ramifications for public health across Europe!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)