
Urgent Call for More Research on Health Literacy and Medication Adherence in Ethnic Minority Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
2025-04-03
Author: Sarah
Introduction
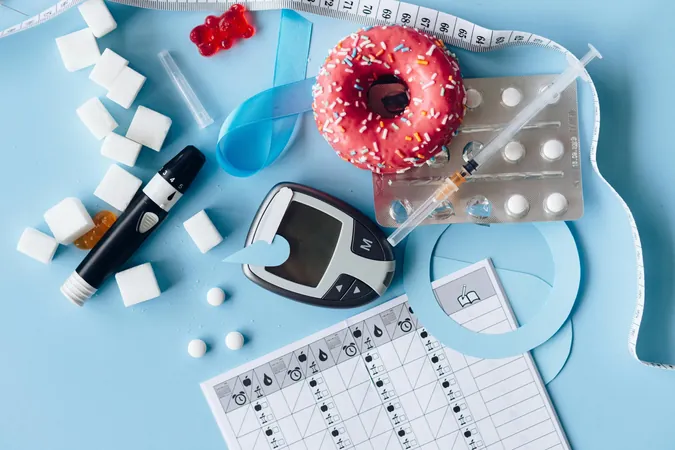
A recent study led by researchers at Western Sydney University has unveiled a troubling gap in our understanding of the connection between health literacy and medication adherence among ethnic minority adults living with type 2 diabetes. The findings, published in the journal BMC Public Health, emphasize the critical need for more focused research in this area.
Study Overview
The research team, collaborating with colleagues from the University of Sydney, analyzed seven global studies that examined the relationship between lower health literacy and reduced medication adherence. Alarmingly, only one study demonstrated a significant link between the two factors, and none of the research has been conducted in Australia, highlighting a pressing gap in local data.
Challenges Faced by Ethnic Minority Patients
Lead author Jinal Parmar, a Ph.D. candidate from Western Sydney University's School of Health Sciences, pointed out the distinct challenges faced by ethnic minority patients in accessing diabetes care. “These communities often encounter cultural and language barriers, alongside low health literacy,” Parmar explained. “Our study indicates a crucial need for targeted strategies to enhance health outcomes for these populations in Western Sydney.”
Advocates for Co-Designed Resources
Experts in health promotion are now advocating for co-designed resources tailored specifically for ethnic minority groups to tackle these issues effectively. “More comprehensive studies are not just necessary globally, but particularly in the Greater Western Sydney area,” Parmar added.
Cultural Safety Training for Healthcare Professionals
Senior author Associate Professor Amit Arora emphasized the need for health services to incorporate cultural safety training for healthcare professionals who provide care to type 2 diabetes patients. He highlighted practical approaches that can be employed in medical practice, such as using visual aids, applying teach-back methods, and simplifying language to ensure patients fully grasp their treatment instructions.
Importance of Empowerment in Patient Care
“Empowering ethnic minority patients by ensuring they understand their diabetes management helps them take informed control of their health,” Professor Arora stressed.
Urgent Need for Research-Driven Insights
The urgency of this research is further underscored by Dr. Tien-Ming Hng, an endocrinologist at Western Sydney Local Health District and a Conjoint Associate Professor at the university’s School of Medicine. Dr. Hng, who works closely with diverse communities in Western Sydney clinics, insists on the need for research-driven insights to enhance patient outcomes. “The prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Western Sydney surpasses that of other metropolitan regions,” he said.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes often requires patients to adhere to multiple medications to meet their health goals, making consistent medication use crucial for success. “Understanding the array of factors that affect medication adherence within specific ethnic groups is vital,” noted Dr. Hng. “Future studies will provide the insights we need to improve care for our patients.
The call for urgent research in this field not only highlights the health disparities facing ethnic minority groups but also sets the stage for future interventions that can make a significant difference in managing type 2 diabetes across culturally diverse communities.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)