Unveiling the Urban-Rural Divide in Healthy Lifestyles Post-COVID: How Social Distancing Changed Behavior in China
2025-01-27
Author: Daniel
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic drastically altered daily life globally, with social distancing measures playing a critical role in curbing the spread of the virus. Following the end of these measures in China on January 8, 2023, researchers sought to uncover how this transition has influenced the health behaviors of urban and rural residents alike. With urbanization on the rise and significant disparities between city and countryside living conditions, understanding these differences post-pandemic provides vital insights for public health interventions.
Study Overview
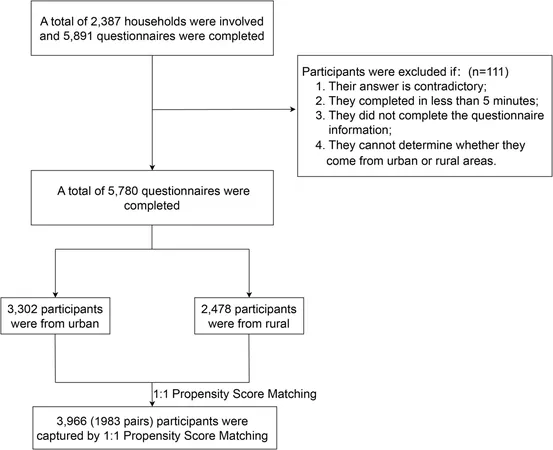
Conducted from February 1 to February 8, 2023, this cross-sectional study involved over 5,700 participants aged 18 and older from four diverse regions: Changzhou (East), Zhengzhou (Central), Xining (West), and Mudanjiang (Northeast). Using a tailored healthy lifestyle behaviors scale containing 11 indicators, researchers aimed to quantify and compare healthy lifestyle habits across urban and rural populations. This methodology allowed for a comprehensive analysis of residents' behavior after the lifting of social distancing, providing insights into the ongoing implications of the pandemic on public health.
Key Findings
A total of 5,780 participants took part, with a significant representation of females (53.04%) and urban residents (57.13%). The average healthy lifestyle behavior score stood at 38.33 on a scale of 11 to 51, highlighting a medium level of adherence to healthy practices. Notably, urban residents scored higher (39.01) than their rural counterparts (37.44), suggesting that even in a post-COVID scenario, urban dwellers maintain healthier behaviors.
Gender disparities were evident; men exhibited lower scores than women in both settings. Furthermore, higher education levels correlated with better lifestyle scores, aligning with previous research that underscores the importance of health literacy. After employing Propensity Score Matching (PSM) to account for confounding variables, the analysis indicated a net difference of 0.87 in healthy lifestyle scores between urban and rural residents, emphasizing the persistent urban advantage.
Lifestyle Behavior Breakdown
The study highlighted varying practices among the urban and rural populations. Urban residents showed superior scores in mask-wearing, social distancing, hand hygiene, diet control, and psychological well-being practices. In contrast, rural residents reported better sleep quality and slight advantages in smoking and drinking behaviors. These findings provoke speculation regarding lifestyle influences unique to urban living, such as economic pressures and resource availability, contrasting with rural residents' cultural and social dynamics.
Implications for Public Health
The research's implications are manifold. Given the inherent health disparities between urban and rural environments, targeted public health strategies are essential to improve health outcomes for rural populations. Educational initiatives promoting the value of healthy lifestyle choices and preventive care, especially in rural healthcare settings, are critical.
Additionally, as rural areas often lack the healthcare infrastructure common in cities, there's a pressing need to bolster medical services and facilitate residents' access to health education on chronic disease management, mental health support, and lifestyle modifications.
Concluding Thoughts
As China recalibrates from the pandemic's grip, this study provides vital evidence concerning lifestyle differences in urban and rural settings that can guide policy and health education efforts moving forward. The findings serve as a rallying cry for health authorities to bridge the gap, ensuring that all Chinese residents, regardless of their geographic location, have the knowledge and resources necessary to pursue healthier lifestyles.
In a world adapting to the lingering effects of COVID-19, these insights offer a beacon of hope for promoting health equity and enhancing the well-being of populations across the spectrum.
Final Note: The ongoing evaluation of health behaviors could be pivotal in shaping effective health policies not just in China, but globally, as disparities in lifestyle practices can profoundly affect the incidence of chronic diseases and overall public health outcomes.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)