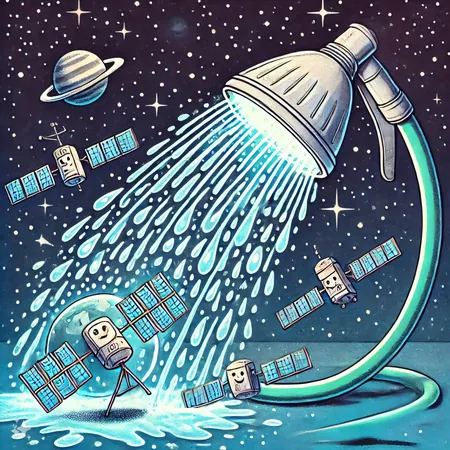

Unveiling the Secrets of Solar Coronal Holes: How They Spritz Solar Wind Like a Cosmic Garden Hose!
2025-04-22
Author: Yu
Solar Coronal Holes: The Cosmic Watering Cans of Our Sun
A groundbreaking collaboration among scientists from the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology, University of Graz, Kanzelhöhe Observatory, and Columbia University has uncovered how coronal holes—vast magnetic openings in the sun's atmosphere—propel fast solar wind streams into the cosmos at jaw-dropping supersonic speeds. This startling revelation not only enhances our understanding of solar dynamics but also prepares us for potential solar storms.
Introducing the Vigil Mission: Your Solar Storm Alert System!
These pivotal findings lay the groundwork for the upcoming Vigil mission, which aims to station itself at the L5 Lagrange point. This solar sentinel will monitor the sun’s wild behavior, offering early warnings of solar storms that could impact vital infrastructure on Earth and beyond. The study's revelations have been published in *Scientific Reports*.
The Sun: More Than Just Light—A Blasting Solar Wind!
The sun doesn’t just emit light; it unleashes a relentless torrent of charged particles known as the solar wind. Traveling at speeds of hundreds of kilometers per second, this high-energy stream showers Earth and the solar system with electrons, protons, and helium nuclei. But beware—this isn’t a gentle breeze; it’s a chaotic river of particles that can create incredible auroras and disruptive geomagnetic storms.
Coronal Holes: Gateway to the Fastest Solar Winds!
The fastest solar wind streams erupt from coronal holes—dark, cooler areas in the sun's outer layer where magnetic fields are stretched wide open, allowing for high-speed solar wind to break free into interplanetary space. The mystery has always been: how do these holes influence the solar winds' behavior?
The Science of Collision: When Solar Winds Meet!
When fast solar wind streams collide with their slower counterparts, they create colossal structures known as corotating interaction regions that spiral outward with the sun's rotation. Because our sun rotates every 27 days, a single coronal hole can continually bombard Earth—a cosmic rhythm of space weather.
A Game-Changer in Space Weather Forecasting!
Led by pioneering solar physicists, the study reveals how coronal holes propel these swift solar winds that crisscross our solar system. This research represents a significant leap in space weather forecasting, extending prediction times from mere hours to several days by utilizing a unique observational position at the L5 Lagrange point.
Solving the Mystery of Solar Wind Measurements!
The team cracked an essential mystery regarding discrepancies in solar wind measurements between L5 and Earth-orbiting L1 observatories. They traced these differences to three key factors: the size of coronal holes, their precise spots on the sun's surface, and the latitudinal position of the spacecraft collecting the data.
The Garden Hose Effect: A Simple Analogy!
As Associate Professor Tatiana Podladchikova explains, "Imagine watering your garden with a hose. If you stand right in front of the stream, you get a deluge. But if you’re off to the side, it’s just a sprinkle. This 'garden hose effect' illustrates why satellites aligned with solar wind streams record higher speeds than those positioned at an angle. Our findings show this effect is particularly strong for smaller coronal holes at higher latitudes, whereas larger holes distribute solar wind more evenly across the heliosphere.
A Bright Future for Solar Research!
This remarkable research not only enhances our capabilities in space weather forecasting but also enriches our fundamental knowledge of the solar-terrestrial environment. Continued exploration from diverse locations like the L5 and L4 points is crucial to fully unravel the sun's monumental influence on our solar system, marking a significant leap forward in the fields of heliophysics and beyond!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)