Unveiling the Mysteries of TOI-2285 b: The Exoplanet on the Edge
2025-05-21
Author: Li
An Exoplanet at a Crossroads
As the hunt for exoplanets accelerates, scientists are uncovering a multitude of celestial bodies, each offering unique insights into the mysteries of climate evolution. Among these intriguing discoveries is TOI-2285 b, an exoplanet that sits precariously at the border between being a super-Earth and a sub-Neptune— a rare cosmic gem.
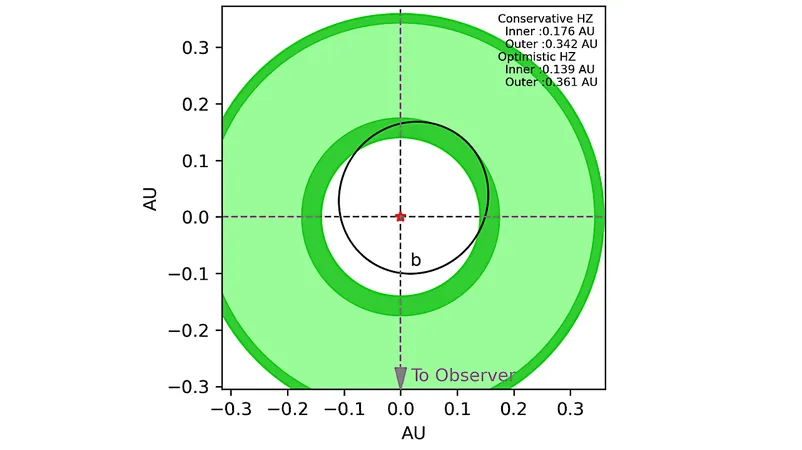
The Venus Zone: A Climate Conundrum
TOI-2285 b exists within both the Habitable Zone (HZ) and the Venus Zone (VZ), making it a prime candidate for studying climatic variations and planetary makeup. This exoplanet (approximately 1.74 times the radius of Earth) experiences significant stellar insolation, providing a rich ground for research into potential evolutionary scenarios.
Inside the Planet: A Deeper Look
To assess TOI-2285 b's potential environments, researchers estimated its volatile components by analyzing its bulk density and interior composition. Using advanced climate modeling software known as ROCKE-3D, they explored various temperate scenarios that could exist on the planet, factoring in different landscapes and initial water distributions.
Diving into Climate Simulations
These climate simulations unveiled fascinating possibilities. The results suggest that despite TOI-2285 b's predicted steam atmosphere, there are scenarios where the planet could maintain a temperate climate, especially when viewed through the lens of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) which modeled transmission and emission spectroscopy for each climate outcome.
Water: The Key to Understanding TOI-2285 b
An intriguing histogram illustrated the potential water content in TOI-2285 b's atmosphere. The findings revealed a bimodal distribution: 29% of the data indicated the planet might be relatively dry, with less than 0.1% of Earth's ocean volume existing as water vapor. Conversely, the remaining 71% suggested a water-rich atmosphere, averaging an astounding 5,260 times the oceans of Earth.
Climate Scenarios Explored
The ROCKE-3D simulations generated six distinct climate scenarios, each based on varying amounts of surface water and topographies reminiscent of Venus, aquaplanets, and Earth itself. The models highlighted temperature variations and water fractions, pinpointing areas likely to be partially covered in ice.
A Step Forward in Exoplanet Exploration
In summary, the analysis of TOI-2285 b not only enriches our understanding of exoplanets straddling the line between terrestrial and gaseous masses but also poses critical questions about the existence of life beyond Earth. As the exploration of our universe continues, TOI-2285 b stands out as a captivating example of what lies beyond our own planet.





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)