
Unveiling the Infinity Galaxy: Cosmic Collision Reveals Secrets of Supermassive Black Holes
2025-07-19
Author: Li
Astronomers Discover the Stunning Infinity Galaxy
Astronomers have made a jaw-dropping discovery using data from the James Webb Space Telescope: an extraordinary cosmic phenomenon dubbed the "Infinity Galaxy." This unique celestial object is the result of a dramatic collision between two galaxies and could hold the key to understanding the formation of supermassive black holes.
A Cosmic Wonderland of Black Holes
According to Pieter van Dokkum, lead author of the latest study published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters, this galaxy is anything but ordinary. "Everything is unusual about this galaxy. Not only does it look strange, but it also boasts a supermassive black hole that’s pulling in massive amounts of material," he revealed. In a stunning twist, both galaxy nuclei harbor their own active supermassive black holes, resulting in a system with three confirmed black holes.
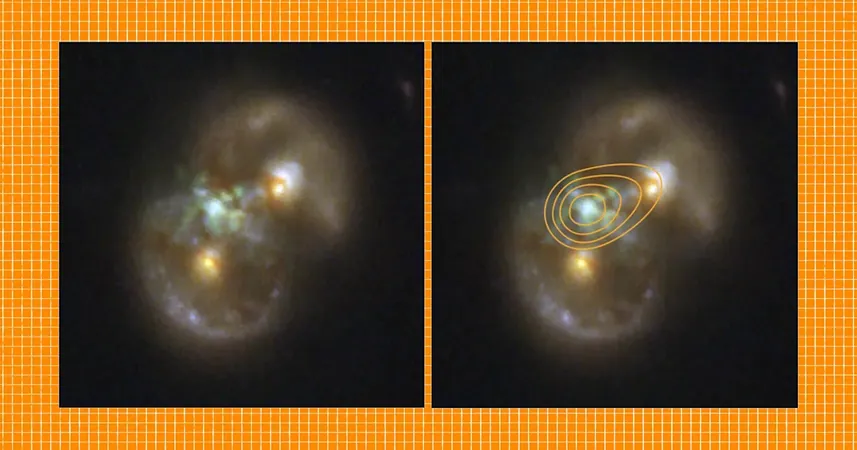
The Enigmatic Shape of Infinity
Captured in stunning images from the Webb telescope, the Infinity Galaxy showcases two luminous spots, each representing the cores of the colliding galaxies surrounded by radiant rings of stars. This striking configuration gives it the iconic shape of an infinity symbol, truly living up to its name.
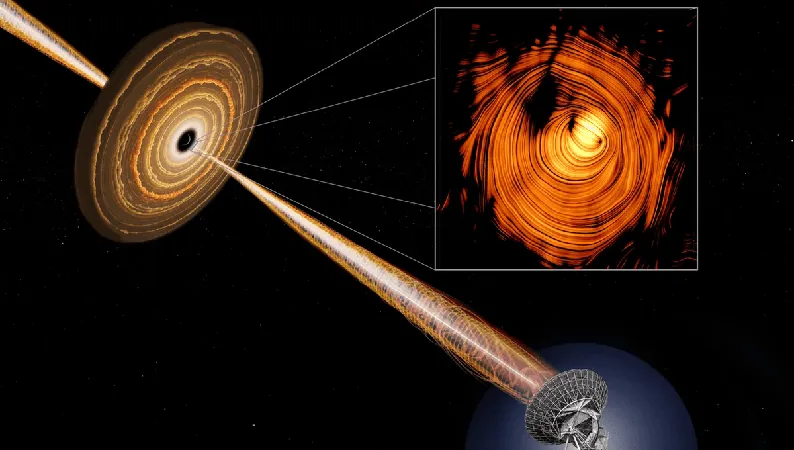
Witnessing the Birth of a Supermassive Black Hole
The most astonishing aspect unveiled by follow-up observations is a colossal supermassive black hole nestled in a swirling sea of ionized gas. It's estimated to have a mass one million times greater than our Sun—and it's still growing. Van Dokkum expressed excitement over the implications of this finding: "We think we're witnessing the birth of a supermassive black hole—something that has never been seen before." This discovery could provide critical insights into black hole formation.
The Great Mysteries of Black Hole Origins
The creation of supermassive black holes remains one of the biggest enigmas in cosmology. They are known to exist and form the hearts of vast galaxies, including our Milky Way, but the processes behind their enormous mass—sometimes reaching hundreds of billions of solar masses—are still fiercely debated.
Traditionally, black holes are thought to form from the collapse of massive stars during supernova explosions, creating black holes a few to a thousand times the size of our Sun. However, this wouldn't explain the existence of observable black holes that existed just 400 million years after the Big Bang, which have masses far exceeding the expected growth time.
Could the Heavy Seed Theory be the Answer?
This discrepancy opens the door to the "heavy seed theory," proposed by van Dokkum. This concept suggests that massive black holes, potentially a million times the mass of our Sun, could form directly from the collapse of enormous gas clouds given the hot conditions of the early universe, allowing a singular large mass to form rather than multiple smaller stars.
Is the Infinity Galaxy the Birthplace of a New Black Hole?
Evidence points toward the Infinity Galaxy as a prime candidate for showcasing this direct-collapse process. The velocity of the central supermassive black hole aligns perfectly with the surrounding gas, indicating it likely formed right at that location. Van Dokkum theorizes that during the collision of the two galaxies, the gas was compressed into a "dense knot"—which ultimately collapsed to create the black hole.
While van Dokkum is cautious, stating, "We can't say definitively that we have found a direct collapse black hole," he emphasizes that these new insights strengthen the argument that we're observing a newborn black hole while eliminating rival theories. This discovery could unravel the secrets of black holes and their incredible evolution in the cosmos.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)