Unveiling the Health-Boosting Secrets of Piper Longum Fruits: A Breakthrough in Functional Foods and Natural Medicine!
2025-03-28
Author: Jia
Introduction
In an exciting development for the realms of nutrition and traditional medicine, researchers are shining a light on the potent health benefits of Piper longum fruits, commonly used as a spice and heralded in traditional Chinese medicine for their ability to combat cold and alleviate pain.
Historical Background
With a rich historical background steeped in medicinal use, the fruits of P. longum present a treasure trove of therapeutic compounds waiting to be discovered. However, extracting novel active compounds from natural products has long posed a significant challenge due to the complex chemical structure of these traditional remedies.
Breakthrough Study
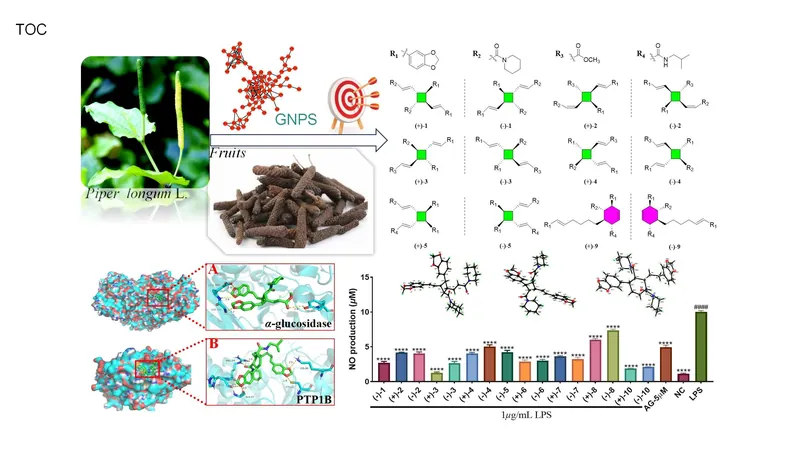
A groundbreaking study led by Prof. Haji Akber Aisa from the Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry, affiliated with the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has successfully navigated this complexity. The research team employed an innovative molecular network-based dereplication strategy to isolate 12 enantiomers of dimeric amide alkaloids from P. longum fruits. Their findings, recently published in the esteemed Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, unveil not just one but multiple compounds with promising anti-inflammatory and antidiabetic properties.
Methodology
Using advanced techniques, the researchers constructed a molecular network from a 95% ethanol extract of P. longum fruits using the GNPS platform's Feature-Based Molecular Networking (FBMN) module. Intriguingly, within their analysis, they identified distinct clusters that contained unexplored molecular weights, with some ranging between 486.191 to 653.255 Da, which did not match any known chemical structures in existing databases.
Key Discoveries
Central to their discovery was a “seed molecule,” piperchabamide H, which spurred the isolation of the 12 dimeric amide alkaloids. These compounds were meticulously separated into 12 pairs of enantiomers using chiral high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), with the structures elucidated through a combination of spectroscopic data, electronic circular dichroism (ECD) calculations, and X-ray diffraction analysis.
Results
The results were astonishing: among the identified compounds, researchers pinpointed eight pairs of cyclobutane-type dimers and four pairs of cyclohexene-type dimers. Remarkably, this study contributed five new cyclobutane-type dimers and one new cyclohexene-type dimer to the existing chemical library.
Bioactivity Screening
Notably, the in vitro bioactivity screening illuminated the potential of these compounds—a promising avenue for health applications. Three of the isolated compounds exhibited significant anti-inflammatory effects in laboratory models that simulate conditions in the human body. Furthermore, one compound was found to effectively inhibit α-glucosidase, while three compounds demonstrated impressive inhibitory activity against protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B (PTP1B), a crucial enzyme often linked to diabetes and obesity.
Molecular Interactions
To understand the underlying mechanisms of these interactions, the team employed molecular docking studies, focusing on the two most active compounds. The research unveiled stable complexes formed between the alkaloids and their target proteins, supported further by molecular dynamics simulations providing additional evidence of stability and interaction efficacy.
Implications
The implications of this research are profound, opening the door for the development of new functional foods and therapeutic agents derived from Piper longum. As scientists continue to unravel the mysteries of traditional medicines, the promising potential of these bioactive compounds could herald a new era of health solutions, combining ancient wisdom with modern science.
Conclusion
Stay tuned as we monitor these thrilling developments that could revolutionize how we think about functional foods and their contribution to our health!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)