Unveiling the Deadly Link: How the Triglyceride-Glucose Index Predicts Mortality in Hypertensive Patients
2025-01-29
Author: Nur
Introduction
Hypertension (HTN) remains one of the world's most pressing health threats, with a staggering prevalence that has ballooned from 650 million in 1990 to 1.3 billion by 2019. Alarmingly, by 2025, an estimated 29.2% of adults are projected to be affected, largely due to population aging. This condition not only increases the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) but also poses a significant threat to overall mortality. Insulin resistance (IR) is a major player in the metabolic dysfunction associated with HTN, yet assessing it effectively remains a challenge. Enter the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index—a promising marker for IR—and its derivatives that may illuminate paths to predict mortality in hypertensive patients.
Study Overview
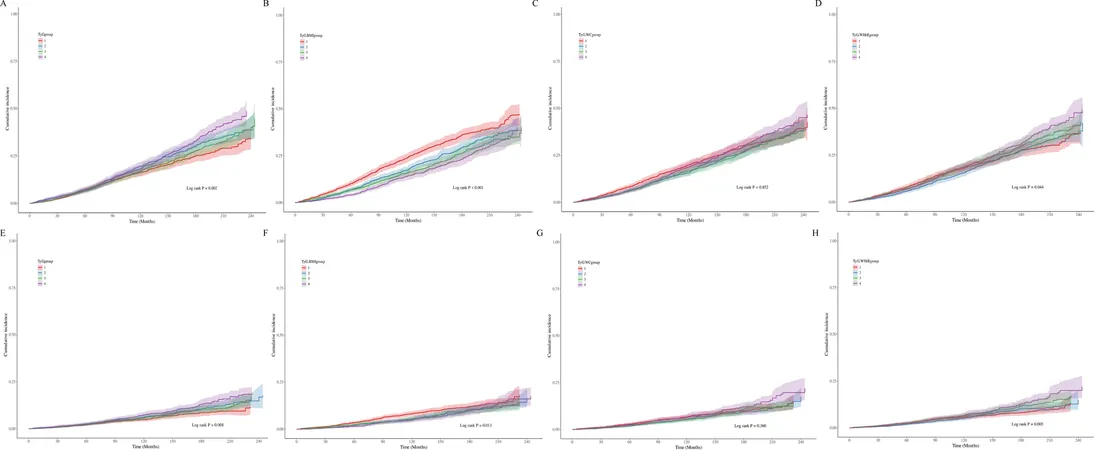
Using data from 9,432 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning from 1999 to 2018, researchers deployed machine learning techniques to explore the relationship between the TyG index and mortality outcomes in hypertensive individuals. They specifically examined the TyG index and its derivatives: TyG-BMI, TyG-WC, and TyG-WHtR, revealing some startling insights.
Key Findings
The study found that the TyG index and its derivatives are not just additional metrics but independent predictors of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Specifically, each incremental increase in the TyG-WHtR was associated with a shocking increase of 41.7% in the risk of all-cause mortality and a staggering 48.1% for cardiovascular mortality. Surprisingly, the analysis revealed that the relationship between these indices and mortality was not linear, indicating that their effects might intensify at certain thresholds.
The Striking Statistics
During an average follow-up of nearly 110 months, the mortality statistics were grim: 2,348 cases of all-cause mortality and 801 cardiovascular deaths among hypertensive patients were reported. These figures reflect an all-cause mortality rate of 27.1 per 1000 person-years—a clarion call for early intervention and risk stratification.
The Pathophysiological Connection
The interplay between HTN and IR is complex, fueling a cycle of cardiovascular risk. IR hampers proper glucose metabolism, leading to excess fat accumulation, which in turn exacerbates metabolic syndrome and increases CVD risk. This cyclical deterioration necessitates timely diagnosis and treatment approaches. The TyG index emerges as a tool that reflects this relationship by combining triglyceride and glucose levels to paint a clearer picture of cardiovascular health risks.
Machine Learning Insights
Employing machine learning approaches, the study unveiled intricate relationships between various health metrics and mortality. This advanced analysis revealed that the TyG index and its derivatives, when included in predictive models, could markedly enhance the accuracy of mortality predictions for those suffering from hypertension.
Comparative Analysis of Prediction Models
Among various models tested, the XGBoost algorithm emerged supreme, exhibiting exceptional predictive accuracy. Integrating the TyG index into clinical decision-making frameworks could significantly improve the identification of high-risk patients, thereby enabling healthcare providers to tailor preventive strategies.
Conclusion
The TyG index and its derivatives are more than just numbers; they are vital indicators that can enhance risk stratification in hypertensive patients. By acknowledging the strong association between these indices and mortality—even after adjusting for confounding factors—we may take significant strides toward improved management and outcomes for hypertensive populations.
A Call to Action
As the burden of hypertension continues to rise, actionable insights gleaned from the TyG index could be the key to intervention strategies aimed at reducing mortality rates. With ongoing research necessary to further validate these findings, healthcare stakeholders must prioritize incorporating these metrics into patient assessments to facilitate timely, life-saving interventions.
Stay tuned as we continue to unveil the hidden dangers of hypertension and innovations in predicting cardiovascular health outcomes!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)