Unveiling the Daily Hormonal Dance: How Men's Hormones May Influence Brain Shrinkage
2024-09-20
Introduction
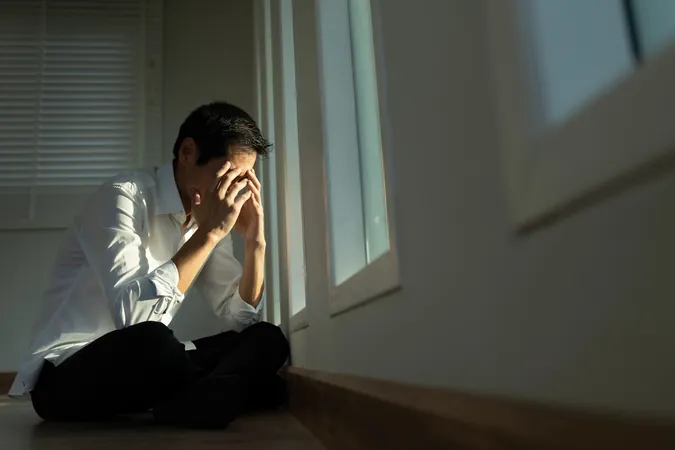
A recent study has revealed an intriguing daily rhythm in men’s hormones that may contribute to the gradual shrinking of their brains from morning to night. The research has drawn connections between fluctuating hormone levels and changes in brain volume, highlighting a phenomenon that has significant implications for our understanding of male biology.
Study Overview
The study analyzed the brain of a 26-year-old male, using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans collected at either 7 a.m. or 8 p.m. over the span of 30 days. This timing was chosen as it coincides with peaks and troughs of steroid hormones such as testosterone, cortisol, and estradiol. “Males experience a striking 70% decrease in steroid hormones from morning to evening,” explained Laura Pritschet, one of the co-authors of the study and a postdoctoral scholar in psychiatry at the University of Pennsylvania.
Gender Differences in Hormonal Fluctuations
While both men and women experience hormonal fluctuations, men exhibit a more pronounced daily rhythm. Women's hormonal cycles, influenced by menstruation, tend to create longer-term shifts rather than a sharp daily ebb and flow.
Findings on Brain Volume
Throughout the day, researchers noted a decrease in both overall brain volume and the thickness of the cerebral cortex, with thickness shrinking by approximately 0.6%. Notably, the parietal and occipital cortices, which are critical for sensory processing and visual perception, experienced the most significant reduction. Changes also appeared in deeper structures such as the cerebellum and hippocampus, which play essential roles in movement coordination and memory formation, respectively.
Debate on Hormones and Brain Size
However, the relationship between hormones and brain size remains a subject of debate. “It’s still uncertain whether hormonal changes are driving these brain alterations,” Pritschet remarked. The research team emphasized the need for further investigation to understand the underlying mechanisms involved.
Historical Context
Historical research has established connections between steroid hormones and brain structure, with some studies showing that fluctuations in reproductive hormones during the menstrual cycle can induce brain changes. The present study adds to this discourse by highlighting significant hormonal variability in men, challenging the long-held belief that such dynamics are primarily relevant to women.
Potential Influence on Brain Function
There is also speculation about whether men’s hormonal cycles could potentially influence brain function. Previous research from the same team indicated that brain connectivity varies according to a 24-hour hormonal cycle, with synchronization among different brain regions fluctuating alongside hormone levels.
Participant Insights
Interestingly, the study’s participant, Pavel Shapturenka, found participating in the MRI scans to be a “relaxing” and “hypnotic” experience. He expressed a desire to contribute to neuroscience, shedding light on male hormonal cycles that aren’t often highlighted in scientific literature.
Future Research Directions
Future endeavors may include examining how variations in sleep patterns affect these hormonal fluctuations and brain functions. Since disrupted sleep is associated with metabolic disorders and mental health issues, understanding the interplay of sleep with daily hormonal and brain cycles could yield valuable insights.
Conclusion
As research progresses, one thing is certain: the daily hormonal cycle is not just a woman's domain; it is time we recognized that men's hormones too possess a rhythm that could fundamentally influence brain dynamics. Stay tuned as science continues to unravel the complexities of human biology!







 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)