Unveiling Hidden Trends: The Rise of Deworming Medication Use Among Pregnant Women in Sierra Leone (2008-2019)
2024-11-04
Author: Sarah
Introduction
In Sierra Leone, the silent but deadly threat of intestinal worm infections poses significant risks to pregnant women, particularly in low and middle-income countries. These infections can lead to severe health complications, including anemia, malnutrition, premature births, and low birth weight. Fortunately, administering deworming medication during pregnancy is a proven method to combat these health issues, enhancing both maternal and child health outcomes. This article explores the dramatic rise in the use of deworming medication among pregnant women in Sierra Leone from 2008 to 2019, highlighting important trends and the persistent inequalities that still exist.
Research Insights
According to the Sierra Leone Demographic Health Surveys conducted in 2008, 2013, and 2019, the prevalence of deworming medication use during pregnancy soared from a mere 43.8% in 2008 to an impressive 83.5% in 2019. This substantial increase signals an important stride toward better maternal healthcare access and public awareness. However, this progress reveals a complex landscape where socioeconomic factors play a key role.
Inequality Trends
While deworming rates have increased, the disparities among different demographic groups remain troubling. Economic-related inequalities slightly intensified; the poorest women experienced the lowest coverage rates. Similarly, educational disparities persisted as women with higher education consistently reported higher usage rates throughout the study period. On the other hand, age-related inequalities surprisingly decreased over time, suggesting targeted efforts may have successfully improved deworming access across age groups.
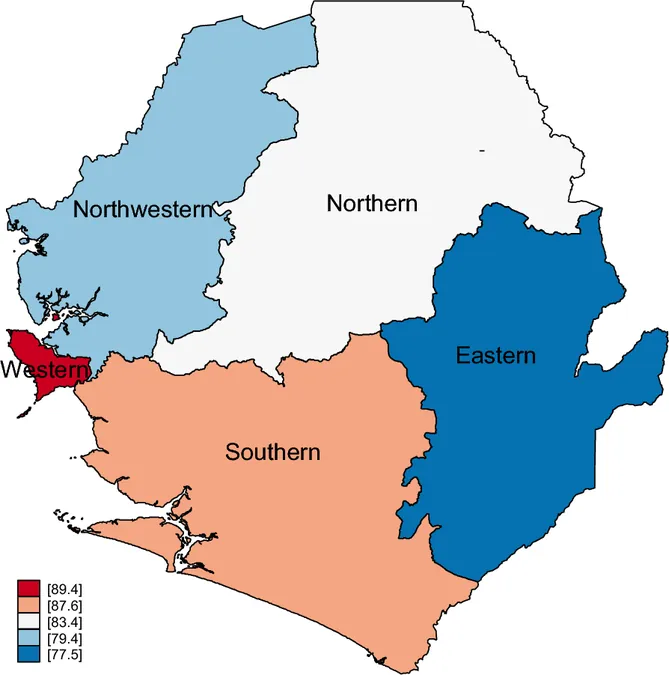
Geographical disparities also manifested interestingly. Urban women had a higher prevalence of deworming medication use compared to their rural counterparts, although both groups demonstrated increases. The rates of deworming medication usage varied between provinces; the Western province emerged with the highest prevalence at 89.4%, while the Eastern province lagged behind at 77.5%.
Global Context
This shocking rise in usage places Sierra Leone in the spotlight among global deworming initiatives. According to the World Health Organization, only about 50% of pregnant women in endemic areas worldwide receive deworming treatment, highlighting the urgency of expanding such interventions. Comparatively, Sierra Leone's achievement of 83.5% in 2019 brings hope, signaling that continuous public health efforts can lead to significant improvements.
Challenges and Policy Implications
Despite the success, many challenges remain. Logistical barriers, inadequate healthcare infrastructure, and medication shortages hinder consistent and widespread deworming initiatives. The government, alongside various organizations, has rolled out public health campaigns to raise awareness and increase access. Yet, continuous efforts are needed to address these challenges proactively.
Targeted policies and community health programs focused on reaching impoverished women and those with lower educational attainment are essential. Engaging local leaders and incorporating culturally sensitive approaches can further enhance help-seeking behavior among pregnant women.
Conclusion
The journey from 2008 to 2019 reflects remarkable progress in the fight against intestinal worms during pregnancy in Sierra Leone, yet it unveils a complex tapestry of inequalities. As the world looks towards achieving universal maternal health coverage, Sierra Leone presents a crucial case study. The importance of sustained efforts in deworming medication distribution cannot be overstated as it’s essential not only for improving maternal outcomes but also for fostering healthier futures for children born into these challenging environments. Continued investment in education and healthcare access will be pivotal in closing the gaps and ensuring no pregnant woman is left behind in the quest for better health.
In conclusion, while Sierra Leone has made monumental strides forward, the need for vigilance and dedicated resources remains crucial to build on these successes and effectively address the inequalities that still influence maternal health interventions. Stay tuned as we follow the developments in this life-saving initiative!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)