Unveiling a Rare Breast Abscess: The Peptoniphilus harei Case Study
2025-09-01
Author: Sarah
A Surprising Discovery in Breast Health
Breast abscesses typically arise from mastitis, but they can also result from various other factors, including malignancies and issues with lymphatic drainage. Risk factors like age, smoking, and diabetes contribute significantly to these infections. While Staphylococcus aureus is the most common culprit behind breast abscesses, cases involving Peptoniphilus harei are extraordinarily rare—only three instances exist globally.
The Endoscopic Surgery Journey
Endoscopic assisted breast surgery (EABS) is revolutionizing breast cancer treatment, offering advantages like smaller, less noticeable incisions and increased patient satisfaction. However, this method isn’t without risks; complications such as skin burns and infections have been documented. Notably, prior to this report, no cases linked Peptoniphilus harei to breast abscess post-EABS.
Case Report: A Shocking Turn of Events
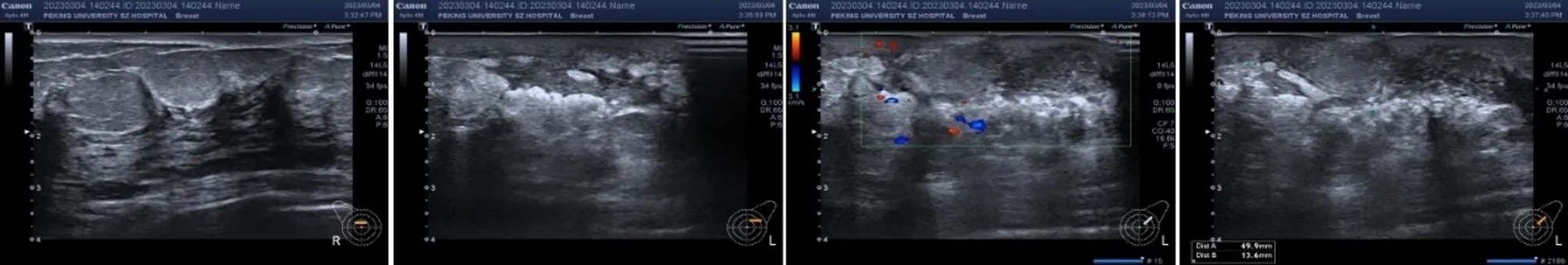
We present the case of a middle-aged woman battling invasive breast cancer. After undergoing chemotherapy and EABS, she faced an unexpected complication: a breast abscess caused by Peptoniphilus harei. Following successful surgery and radiotherapy, the patient noticed symptoms like redness and swelling in her left breast three months post-treatment, leading her to seek medical help.
Diagnosis and Management Challenges
Initial examinations suggested a localized skin infection. When topical treatments failed, the patient's condition deteriorated, culminating in a ruptured skin lesion that expelled foul-smelling fluid. Diagnostic tests ruled out tuberculosis, while a culture eventually revealed the presence of Peptoniphilus harei. This marked the first documented case where this bacterium was the sole cause of a breast abscess.
Innovative Treatment Strategies
A multidisciplinary team introduced an aggressive antibiotic regimen of penicillin and metronidazole, later adjusted to cefazolin after initial treatments showed promising results. As the patient's condition improved, surgical interventions aimed at managing the extensive necrotic tissue were conducted, albeit with careful consideration to minimize further complications.
Implications and Insights
This unique case sheds light on the critical nature of accurately identifying pathogens in postoperative infections, especially concerning breast cancer surgeries. Effective microbial treatment not only influences patient recovery but also helps prevent complications such as recurrent infections and potential cancer relapse.
Looking Ahead: The Importance of Adaptability in Treatment
Though Peptoniphilus harei infections are rare, their implications can be significant, particularly after invasive procedures like EABS. Recognizing the evolving landscape of postoperative care and being prepared for unexpected challenges is essential for optimal patient outcomes. This case serves as a reminder of the importance of thorough microbial assessments in surgical recovery.
A Patient's Journey Towards Recovery
Ultimately, despite the unique challenges presented by her condition, the patient experienced a successful recovery without additional surgeries for breast reconstruction. Her experience highlights a growing narrative in breast health concerning complex infections and the promise of modern surgical techniques.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)