Unraveling the Secrets of 'Selfish' B Chromosomes: A Breakthrough in Rye Genetics!
2024-11-11
Author: Wei Ling
Introduction
In a groundbreaking discovery, an international team of researchers led by the IPK Leibniz Institute has shed light on the enigmatic B chromosomes in rye - a peculiar genetic phenomenon that can enhance its own inheritance at the expense of the organism’s overall genetic health. These extra chromosomes, known for their 'selfishness,' have fascinated scientists for decades, as they can be found in nearly 3,000 species across the spectrum of eukaryotes.
Differences Between B and A Chromosomes
B chromosomes differ significantly from the standard A chromosomes, which are essential for the normal development and functionality of organisms. While A chromosomes carry vital genes for growth, B chromosomes are often non-essential and can lead to various complications, including fertility issues and phenotypic abnormalities when present in larger numbers.
Challenges in Studying B Chromosomes
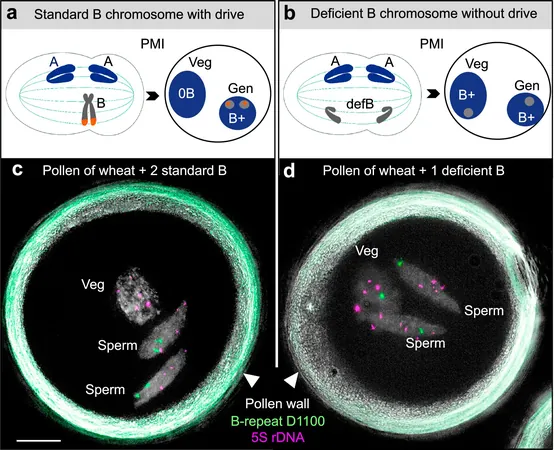
The significant challenge in studying B chromosomes has been their complex structural nature, often marked by repetitive sequences that complicate genome assembly. Historically, despite the scientific advancements brought by the DNA sequencing revolution, researchers struggled to pinpoint the specific mechanisms that enable these rogue chromosomes to thrive. Many B chromosomes utilize a strategy known as 'chromosome drive,' allowing them to multiply during cell division to maintain their presence, often disregarding the host organism's well-being.
Breakthrough in Research
In this recent study published in Nature Communications, researchers successfully honed in on the genetic machinery controlling this drive mechanism within the rye's B chromosome. By leveraging advanced long-read sequencing technology, they assembled the B chromosome into a single ~430 Mb-long pseudomolecule. This achievement represents significant progress in genetic research, offering unprecedented insights into these elusive genetic elements.
Discovery of Key Genes
The researchers identified five candidate genes that may play pivotal roles in regulating B chromosome behavior, with the standout gene being DCR28. According to Prof. Andreas Houben, a leading figure in the study, the identification of DCR28 opens new avenues for understanding how B chromosomes exert their influence and manipulate inheritance.
Implications for Genetic Research
Not only does this research unveil the complexities of rye B chromosomes, but it also potentially paves the way for broader implications in genetic studies, particularly in understanding genetic diseases related to chromosome imbalances. As scientists continue to decode the intricacies of these 'selfish' chromosomes, we may gain deeper insights into genetic stability and inheritance mechanisms in various organisms.
Conclusion
This exploration into the genetic world of B chromosomes raises exciting questions about evolutionary strategies and the ongoing struggle between beneficial and detrimental genetic elements. As we stand at the brink of genomic discovery, one thing remains clear: the secrets of the 'selfish' B chromosomes continue to unravel, promising a brighter future for genetic research!
Call to Action
Stay tuned for more updates on this captivating field of study!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)