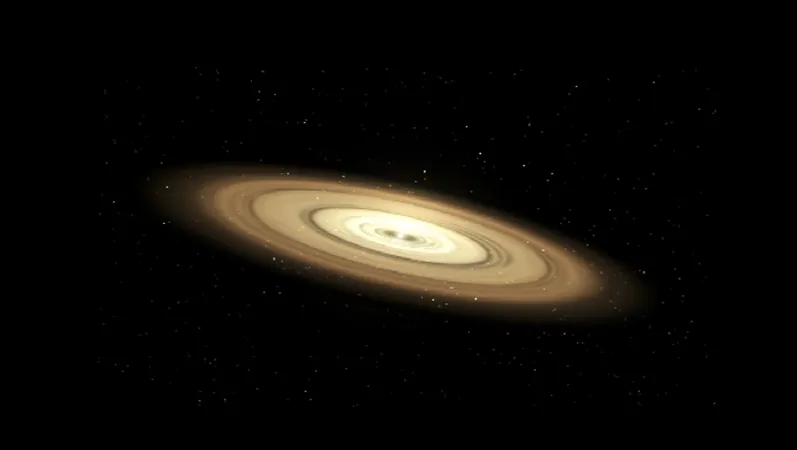

Unraveling the Secrets of Exoplanet Formation: The Role of Pebble Accretion
2025-05-03
Author: Ming
The Pebble Accretion Hypothesis: A Game Changer for Exoplanet Formation
Pebble accretion has emerged as the frontrunner explanation for how exoplanets, particularly those more massive than Earth, take shape in the cosmos.
The Key Factors in Planet Growth
Several critical parameters dictate the development of planets in the context of pebble accretion. A recent study delves into how factors such as pebble fragmentation velocity, turbulence strength, stellar metallicity, stellar mass, and the planet’s location—all play pivotal roles in the evolution of planets located within one astronomical unit of their parent stars.
Turbulence: A Crucial Influence on Planet Formation
In analyzing close-orbiting planets from NASA’s Exoplanet Archive, researchers uncovered that turbulence strength has a greater impact on planet growth compared to pebble fragmentation velocity.
The Metallic Advantage: Higher Chances for Planetary Growth?
The findings suggest that planets orbiting stars with elevated metallicity have a significantly greater chance of accumulating enough material to reach what scientists call "pebble isolation mass." However, this metallicity advantage is overshadowed by the more considerable influences of stellar mass, orbital separation, and especially, disc turbulence.
What This Means for Future Research
This ground-breaking research not only enhances our understanding of planetary formation but also opens new avenues for investigations into how different stellar environments can affect the likelihood of planet formation. With more discoveries on the horizon, the cosmos continues to reveal its mysteries—all thanks to studies like these!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)