Unraveling the Secrets of Atmospheric Rivers in Antarctica: What You Need to Know!
2025-06-02
Author: Li
Unlocking Antarctica's Climate Mysteries
A groundbreaking study, spearheaded by Irina Gorodetskaya from the Interdisciplinary Center of Marine and Environmental Research (CIIMAR), has compiled crucial new data on atmospheric rivers in Antarctica, shedding light on the complexities posed by climate change.
The Hidden Power of Atmospheric Rivers
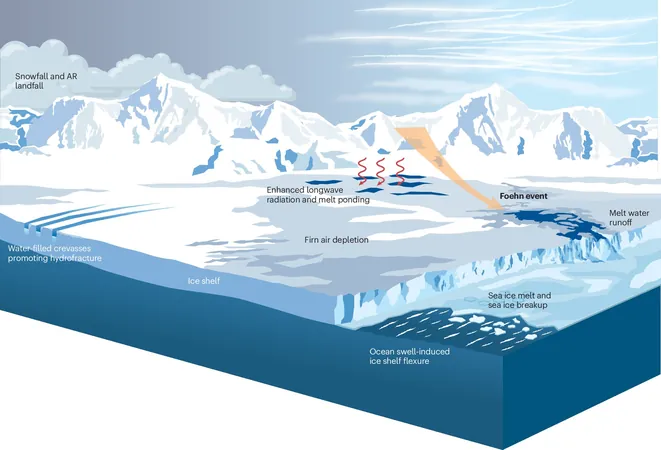
Atmospheric rivers are striking phenomena—long, narrow channels of moisture that transport heat and water from tropical regions all the way to the poles. Over the last decade, our understanding of these climate drivers has evolved dramatically, thanks to the collaborative effort of researchers from 10 countries, led by Gorodetskaya alongside Jonathan Wille (ETH, Switzerland) and Vincent Favier (IGE, France). Their findings are encapsulated in the article "Atmospheric rivers in Antarctica," recently published in *Nature Reviews Earth & Environment*.
Impact on Polar Climate
These atmospheric rivers play a pivotal role in shaping humidity, precipitation, and temperature in polar zones. Antarctica, home to over 90% of the world’s fresh surface water, is notably influenced. While recent findings suggest that these rivers can contribute positively by increasing snowfall and maintaining ice sheet balance, they also exacerbate melting and instability, leading to alarming mass loss from the Antarctic ice sheets—up to 150 billion tons annually since 1992!
According to Gorodetskaya, "Atmospheric rivers serve a dual purpose: they can bring vital snowfall that counteracts mass loss but also induce melting and destabilization, contributing to a significant net loss of ice."
Dynamic Forces at Play
The study delves into various dynamic atmospheric patterns unique to this region, influencing both the formation of atmospheric rivers and their trajectories toward Antarctica. Key factors include tropical convection and local phenomena such as Foehn winds.
What Lies Ahead?
As climate change continues to escalate, the intensity of atmospheric rivers is expected to strengthen due to increased atmospheric water vapor. Although the large-scale snowfall these rivers produce offers some respite, it’s crucial to recognize that they also lead to detrimental melting and destabilization of ice shelves.
Gorodetskaya warns, "Assessing the ultimate impact is a challenge, compounded by a range of non-linear effects. Recent research indicates that while the current contribution of melting from atmospheric rivers to overall Antarctic mass balance is minor, it has the potential to become significant as global temperatures rise."
The Call for Continued Research
To confront these uncertainties, ongoing research and modeling are essential for grasping how atmospheric rivers will respond in our changing climate. Understanding their relationship with Antarctic ice mass balance is vital to refine future climate projections and gauge Antarctica's role in global sea-level rise.
Stay tuned, as science unravels more about these astonishing weather systems and their far-reaching effects on our planet!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)