Unraveling the Mysteries of Teegarden's Star: A Look into its Coronal and Chromospheric Activity
2025-04-04
Author: Siti
Introduction
Teegarden's star, a late-type M-dwarf, has garnered significant interest due to its potential for hosting planets and intriguing activity levels. This study dives deep into the characterization of Teegarden's stellar activity at various atmospheric levels: photospheric, chromospheric, and coronal.
Recent Observations
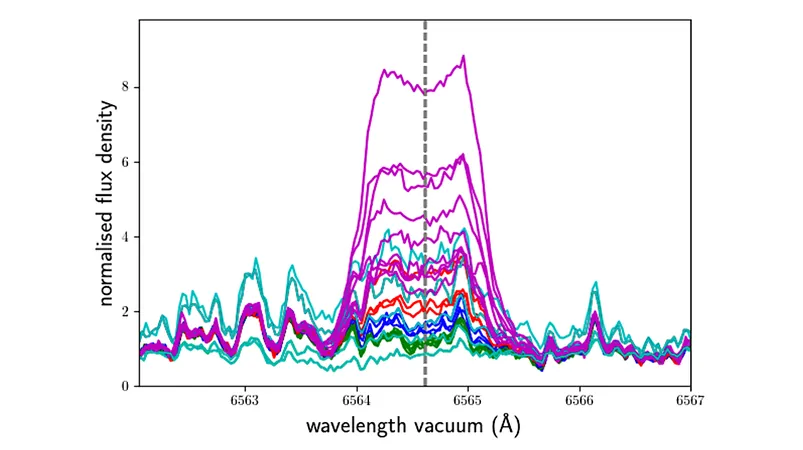
Recent observations from NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) revealed two exceptionally large flares, with flare fluences estimated between 10²⁹ and 10³² ergs—sizes comparable to the most powerful solar flares known to us. An analysis of nearly 300 CARMENES spectra alongside 11 ESPRESSO spectra has provided a detailed view of the star’s chromospheric lines, ranging from the classic Ca ii H & K lines at 3930 Å to the enigmatic He i infrared triplet at 10830 Å.
Chromospheric Line Behavior
The findings of the study reveal varying behaviors among these chromospheric lines. Notably, the He i triplet was absent across all observed spectra. Some lines appeared exclusively during flares, while others exhibited a constant presence with notable variability. For instance, the Hα line often appeared filled during quieter periods, yet higher Balmer lines consistently emitted.
Correlation with Star Rotation
Furthermore, many of the chromospheric lines demonstrated a correlation with the variability of Hα, indicating not only random fluctuations but also systematic changes linked to the star’s rotation period. This comprehensive analysis also uncovered multiple flares and even suggested the presence of an erupting prominence, potentially resulting in a coronal mass ejection—a significant event indicating dynamic processes at play.
X-ray Observations
Adding another layer to this investigation, X-ray observations carried out with the renowned Chandra Observatory and the XMM-Newton Observatory offered further insights. One of the large flares presented clear evidence of the Neupert effect, hinting at the generation of hard X-rays during these explosive events.
Implications for Astrobiology
These revelations not only enhance our understanding of Teegarden's star's atmosphere but also provide crucial data that could inform astrobiological studies, particularly regarding the potential habitability of planets that might orbit such an active star.
Conclusion
This extensive research, conducted by a team of experts in stellar astrophysics, opens the door for future investigations into the magnetic behaviors of M-dwarfs and their implications for surrounding planetary systems. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the mysteries of the cosmos!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)