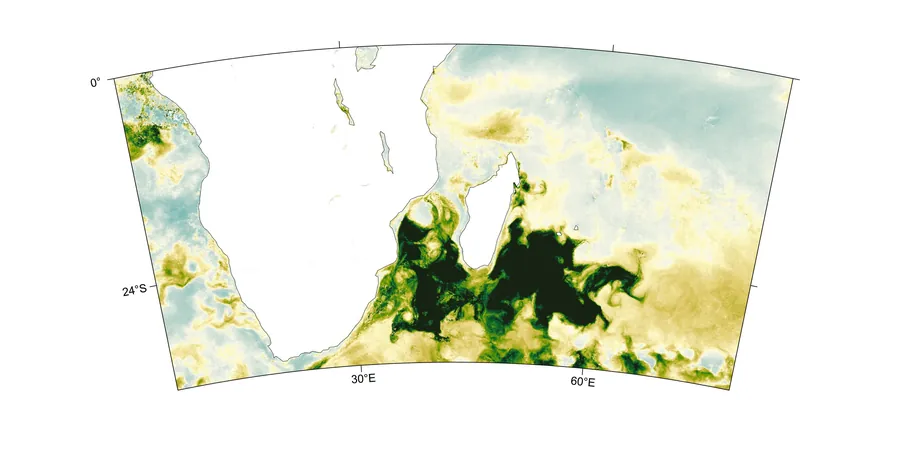
Unprecedented Dust from Southern Africa Fuels Phytoplankton Explosion off Madagascar’s Coast
2024-10-01
Introduction
A groundbreaking study has revealed a striking connection between severe droughts in Southern Africa and a remarkable bloom of marine phytoplankton off the southeast coast of Madagascar. Researchers have determined that the increased frequency of droughts, a trend exacerbated by climate change, can lead to significant ecological shifts in distant oceanic regions.
Research Findings
The research team, led by Dionysios Raitsos, demonstrated that the dust carried from arid landscapes in Southern Africa acted as a natural fertilizer, stimulating one of the largest phytoplankton blooms recorded in the area between November 2019 and February 2020. Utilizing advanced data from the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) and measurements from a nearby Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) station, the scientists meticulously traced the flow and concentration of dust particles over time.
Dust Impact on Phytoplankton
Remarkably, data indicated that the aerosol optical depth anomalies over the affected bloom region were the highest observed in over 17 years of monitoring. Coinciding with heavy rainfall, these iron-rich dust particles were deposited into the waters, essentially creating a nutrient-rich environment for phytoplankton proliferation. The implications of this study highlight complex interactions between terrestrial droughts and marine ecosystems, as dust generated from areas experiencing high temperatures and prolonged dry conditions may significantly impact ocean chemistry and biological activity.
Future Implications
Experts warn that as global temperatures continue to rise, we may anticipate more frequent and intense phytoplankton blooms caused by similar mechanisms. These blooms not only play a critical role in the marine food web, but they also have the potential to absorb substantial amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thereby influencing climate dynamics.
Conclusion
This research underscores the intricate relationships within Earth's climate system and points to the urgent necessity for more comprehensive studies on how terrestrial changes can ripple through to oceanic outcomes, ultimately affecting global environments and ecosystems.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)