Unmasking the Hidden Threat: The Emergence of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Adult Emergency Departments This Winter
2025-03-17
Author: Wei Ling
Introduction
As public focus remains primarily on well-known respiratory viruses like Influenza and SARS-CoV-2, the burden of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) in adults, particularly during the 2023/2024 winter season, has been shocking yet underreported. Understanding the prevalence, severity, and risk factors associated with RSV is vital as its potential to affect high-risk populations increases.
Methods
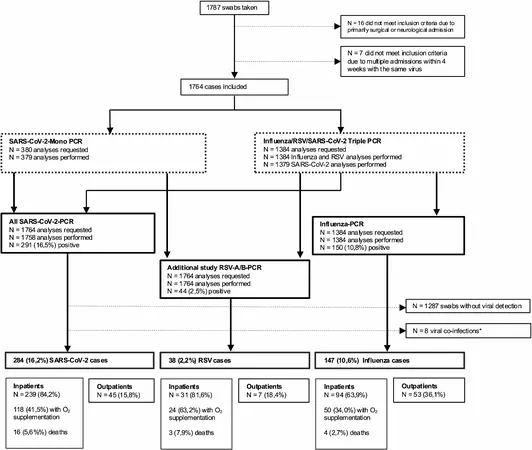
In a groundbreaking prospective observational study at the University Hospital Dresden, researchers analyzed RSV infections among consecutive adult patients diagnosed with acute respiratory tract infections from October 1, 2023, to April 15, 2024. This study utilized nasopharyngeal and pharyngeal swabs to confirm RSV presence through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing, aiming to provide insights into this often-overlooked virus.
Results
Of the 1,764 patients analyzed (56.3% male, median age 69), a staggering 27.1% tested positive for viral infections, with only 2.2% confirming RSV A or B infections, compared to higher rates of SARS-CoV-2 (16.2%) and Influenza (8.4%). Notably, patients with RSV showed a significantly higher need for oxygen support (63.2%) than those infected with Influenza (34.0%) or SARS-CoV-2 (41.5%). Alarmingly, in-hospital mortality was highest in the RSV cohort at 7.9%, a concerning indicator compared to Influenza (2.7%) and SARS-CoV-2 (5.6%).
Conclusions
While RSV infections were less frequent among adult emergency department patients in the winter of 2023/2024, the severity of illness it caused was alarming. Individuals diagnosed with RSV not only required more respiratory support but also exhibited a notable mortality rate, highlighting RSI as a crucial clinical concern.
Despite being typically associated with children, recent studies reveal a significant burden of RSV in older adults, particularly those with existing health complications. Recent reviews indicate that RSV infections occur in 3-7% of older adults annually, with resulting hospital admissions reaching 12%. In Europe alone, it's estimated that RSV accounts for around 270,000 hospitalizations and 20,000 deaths among adults over 60 each year.
Recent German data reinforces these findings, showing elevated hospitalization rates, intensive care unit admissions, and mortality rates associated with RSV when compared to other respiratory viruses. A shocking 22.4% of patients over 50 hospitalized with RSV experienced acute cardiac events, indicating a troubling link between RSV and cardiovascular complications.
The fight against RSV is pressing, especially as there are currently limited treatment options available. However, promising vaccine developments demonstrate over 80% efficacy in preventing RSV in older adults. Ongoing surveillance for RSV among at-risk populations remains critical to inform public health responses and vaccination recommendations.
Statistics Reveal
This winter has underscored the need for awareness surrounding RSV’s impact on adult populations, especially as seasonal variances in incidence can yield spikes in infection rates. With data from the 2022/2023 winter highlighting particularly high transmission, further research is essential to understand RSV's trajectory in the coming seasons.
In summary, RSV is emerging as a significant public health threat among adult patients with respiratory infections. Healthcare providers and the public must remain vigilant in recognizing its potential severity and advocating for vaccination strategies that could mitigate this viral menace. The data emerging from studies like these will shape how we approach respiratory illnesses in the future.
Stay tuned as we continue to follow ongoing developments in the fight against RSV and monitor the trends in respiratory illness, because knowledge is power and the health of our vulnerable populations depends on it!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)