Unlocking Titan's Secrets: How Does this Enigmatic Moon Maintain its Atmosphere?
2025-01-29
Author: John Tan
Introduction
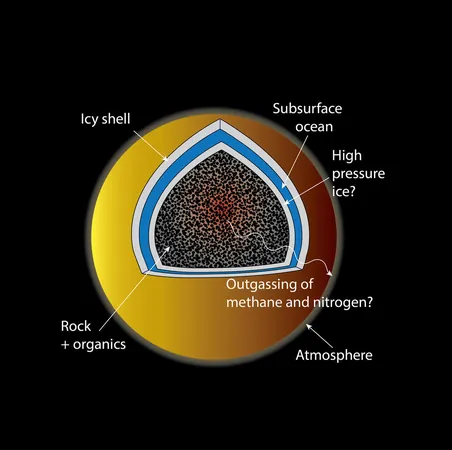
Saturn's moon Titan stands out as one of the most intriguing celestial bodies in our solar system. As the second-largest moon, only eclipsed in size by Jupiter's Ganymede, Titan is singular in having a substantial atmosphere, predominantly composed of 95% nitrogen and 5% methane. This atmosphere is approximately 1.5 times denser than Earth's, compelling scientists to delve deeper into its mysteries.
The Mystery of Methane
One of the most perplexing phenomena regarding Titan is the presence of methane in its atmosphere. This gas typically degrades within 30 million years, raising eyebrows among researchers as to how Titan has managed to sustain such levels without freezing over. The suspicion arises that an unknown internal process is constantly replenishing methane—an area ripe for investigation.
Recent Studies
Recent studies, led by Dr. Kelly Miller from the Southwest Research Institute, emphasize that despite being just 40% the diameter of Earth, Titan's atmosphere remains remarkably robust. Dr. Miller humorously noted, "Even with lower gravity, walking on Titan's surface would feel like you're scuba diving!" This vivid comparison accentuates the uniqueness of Titan's environment.
Groundbreaking Model
Research conducted in collaboration with the Carnegie Institution for Science has yielded a groundbreaking model proposed in 2019. This model suggests that Titan's interior may be heating large organic materials, which, in turn, releases nitrogen and methane gas. This gas then escapes to the surface, replenishing the atmosphere and maintaining its dense characteristics.
Experimental Simulations
To simulate these conditions, Miller's team conducted experiments that mimicked the subsurface environment of Titan by heating organic materials to extreme temperatures of 500 degrees Celsius under high pressure. The results indicated that the methane produced was sufficient to account for the levels observed in Titan's atmosphere today.
The Dragonfly Mission
Excitingly, NASA's ambitions to explore Titan are set to take a monumental leap forward with the upcoming Dragonfly mission, scheduled to launch in 2028. Dragonfly features an innovative quadcopter design, allowing it to navigate Titan's thick atmosphere akin to how Ingenuity maneuvered on Mars. This mission is expected to offer unprecedented insights into Titan's atmospheric dynamics while searching for prebiotic molecules and assessing the moon's potential habitability—an endeavor that could unravel clues about life beyond Earth.
Conclusion
As we eagerly await the Dragonfly mission, Titan continues to captivate our curiosity, offering a tantalizing glimpse of planetary processes and the potential for life in the universe. What other secrets does Titan hold? Only time will tell!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)