Unlocking the Secrets of Your Gut: How Defensin Genes Could Revolutionize Diabetes and Obesity Treatments
2025-09-12
Author: Arjun
Groundbreaking Discovery in Gut Health
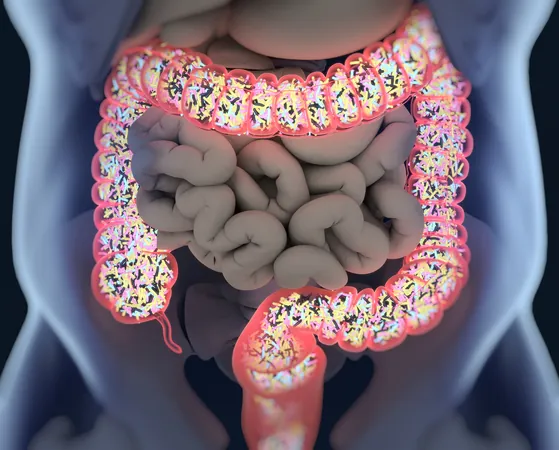
Researchers at the University of Sydney have unveiled a fascinating link between specific genes and gut health, illuminating a path towards better prevention and treatment of metabolic diseases like obesity and diabetes. The study highlights the role of alpha-defensins, special proteins that our bodies produce to maintain a healthy gut microbiome.
The Microbiome Market Boom
Interest in the human microbiome is surging, with the global market set to expand dramatically—from $0.91 billion in 2024 to an estimated $1.4 billion by 2025, and a staggering $7 billion by 2031. This explosive growth underscores the significance of gut health in modern medicine.
Are We Just Hosts For Gut Bacteria?
Stewart Masson, PhD, a lead researcher at the Charles Perkins Centre, emphasizes that while gut microbes influence various chronic conditions, we are not merely passive hosts. Our bodies actively shape our microbial inhabitants.
The Study's Surprising Findings
Published in the EMBO Journal, the research involved initial observations of how certain genes affected insulin resistance in mice. Surprisingly, they found that mice less prone to insulin resistance also had defensin genes encouraging the production of protective proteins.
Defensins: Nature's Immune Building Blocks
Masson explains that defensins have existed across various species, from plants to humans, forming a crucial component of our immune defenses. The study identified a specific location on a chromosome containing 17 defensin genes, which humans and mice share, suggesting a common evolutionary purpose.
A Closer Look at Defa26
Utilizing advanced genetic analysis, the team pinpointed alpha-defensin 26 (Defa26) as the critical gene responsible for producing these protective peptides. To test their hypothesis, they synthesized the Defa26 protein and conducted experiments on two groups of mice with differing natural levels of Defa26.
The Double-Edged Sword of Supplements
While mice lacking Defa26 showed significant improvements in insulin sensitivity after supplementation, those with naturally high levels experienced adverse effects, such as low insulin levels and muscle wasting. This highlights the potential perils of generalized treatments.
The Case for Personalized Medicine
Masson stresses the importance of personalized medicine, advocating for tailored treatments based on individual genetic make-up instead of a one-size-fits-all approach. Understanding these complexities could revolutionize how we treat chronic conditions linked to gut health.
Future Research Directions
The research team is eager to investigate how defensins impact humans, particularly in gauging these proteins within the gut and their effects on metabolic health. David James, PhD, co-author of the study, warns that while precision medicine holds promise, we must tread carefully to avoid hasty alterations to our unique microbiomes.
Conclusion: A New Era of Healthy Living
As we stand on the brink of a new era in health science, this groundbreaking research serves as a reminder of our intertwined destinies with the microbiome. The potential for innovative, individualized treatments is at our fingertips—it's an exciting time for the future of health and wellness!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)