Unlocking the Secrets of the Universe: Machine Learning Revolutionizes the Study of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons!
2025-03-14
Author: Jia
Unlocking the Secrets of the Universe: Machine Learning Revolutionizes the Study of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons!
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) play a pivotal role in our understanding of the universe, especially when it comes to the enigmatic aromatic infrared (IR) bands found in interstellar space. Yet, existing spectral databases for IR emission analysis have been severely hindered by the exclusion of vibrational anharmonicity and temperature effects. This limitation can largely be attributed to the daunting computational costs of traditional quantum chemical calculations (QCCs).
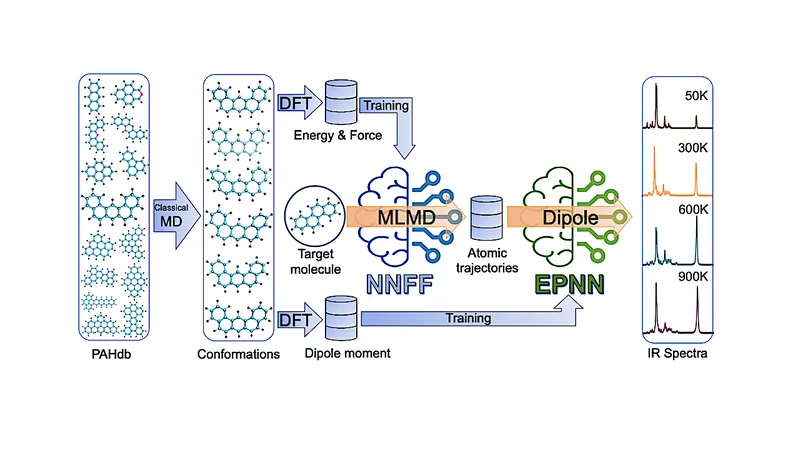
Enter an innovative solution: a groundbreaking machine learning-based molecular dynamics (MLMD) approach! This cutting-edge methodology enables the efficient computation of anharmonic IR spectra while seamlessly factoring in temperature effects. Remarkably, MLMD not only preserves predictive accuracy on par with that of conventional QCCs, but it also operates with a significantly lower computational burden, scaling linearly with the number of atoms in the molecular system.
In an impressive study, the MLMD approach was applied to the analysis of 1704 PAHs from the NASA Ames PAH IR Spectroscopic Database, which includes complex molecules boasting up to 216 carbon atoms. This bold move has paved the way for high-throughput spectral calculations of extensive molecular systems, highlighting the technology's immense potential in astronomy.
The significance of these findings is monumental, especially with the eagerly anticipated data from the James Webb Space Telescope on the horizon. As this extraordinary telescope promises to unveil cosmic mysteries, our enhanced understanding of PAHs through MLMD could give scientists invaluable insights into the chemical makeup of far-off celestial bodies.
Additionally, the study visualizations are striking! They include detailed schematics illustrating the operation of neural networks (NNFF and EPNN) during inference, alongside comparisons of NNFF-predicted atomic forces and EPNN-predicted dipole moments against DFT-calculated reference values for 3,580 tested PAH configurations.
Stay tuned for further advancements in molecular spectral datasets that will transform data-driven analyses of astronomical IR spectra and deepen our comprehension of the cosmos! The journey of discovering new worlds starts here!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)