
Unlocking the Secrets of Tea: New Genetic Discoveries Could Transform Your Cup!
2024-12-26
Author: John Tan
Unlocking the Secrets of Tea: New Genetic Discoveries Could Transform Your Cup!
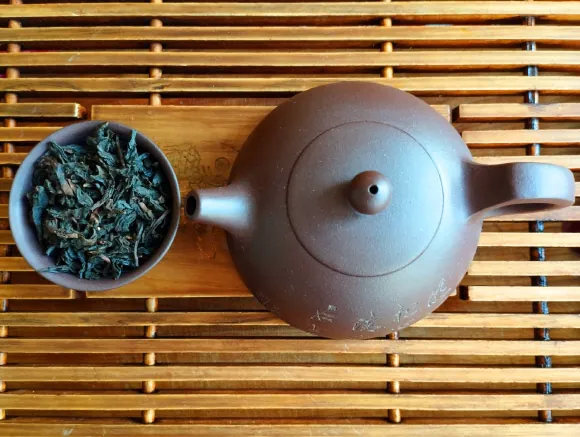
In a groundbreaking study, researchers have unveiled significant insights into the genetic composition of tea that could redefine its quality and health benefits. A team from the Tea Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Huazhong Agricultural University explored the impact of free amino acids (FAAs) on tea, focusing primarily on theanine—the compound responsible for the delightful umami flavor in tea.
The study analyzed 339 different tea varieties, revealing that the concentration of FAAs varies markedly across these types. This variation not only influences the taste but also the nutritional profile of the tea, highlighting the need for deeper understanding and conservation of tea germplasm.
Dr. Liang Chen, co-senior author of the study, emphasized the importance of tea, stating, "Tea (Camellia sinensis) has become one of the most widely consumed non-alcoholic beverages globally, tracing back to its roots in southwestern China." This enormous cultural significance is complemented by the numerous health benefits attributed to tea, from improving heart health to aiding digestion.
The researchers found that secondary metabolites, including polyphenols, catechins, caffeine, and theanine, play a pivotal role in determining the overall quality and flavor of tea. Particularly interesting were the unique cultivars such as albino and purple tea, which contain elevated levels of beneficial secondary metabolites. The findings suggest that albino tea cultivars, which sport striking white and yellow leaves, could have higher theanine concentrations, potentially helping to combat various health issues like obesity and inflammation.
Notably, the research identified the phytochrome interacting factor 1 (CsPIF1) as a key regulator of theanine levels. By knocking down the expression of CsPIF1 in tea plants, researchers observed a marked increase in theanine content—an exciting breakthrough that opens the door for gene editing initiatives aimed at enhancing the flavor and health properties of tea.
Dr. Chen further stated, "Our research significantly broadens the horizon of possible breeding strategies. By manipulating CsPIF1 and related genes, we could see improved theanine levels that would enhance both the nutritional and sensory attributes of tea."
These findings, published in the journal *Horticulture Research*, not only enhance our understanding of tea genetics but could also revolutionize the tea industry, providing breeders with innovative tools to craft teas that resonate with health-conscious consumers and flavor enthusiasts alike.
As the world continues to embrace tea as a staple drink, these scientific developments signal a new era of innovation that could change the way we savor one of our favorite beverages.
Stay tuned as more discoveries unfold, and don’t miss out on potential new varieties that could soon be gracing your cup!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)