Unlocking the Secrets of Serum LDH: Your Liver Health May Depend on It!
2025-07-01
Author: John Tan
A Deep Dive into the NHANES Database
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database serves as a treasure trove of data regarding the health, nutrition, and demographics of individuals across the U.S. This publicly accessible resource strictly follows ethical guidelines to ensure participant consent and provides invaluable insights into the health conditions affecting the population.
Study Focus and Population
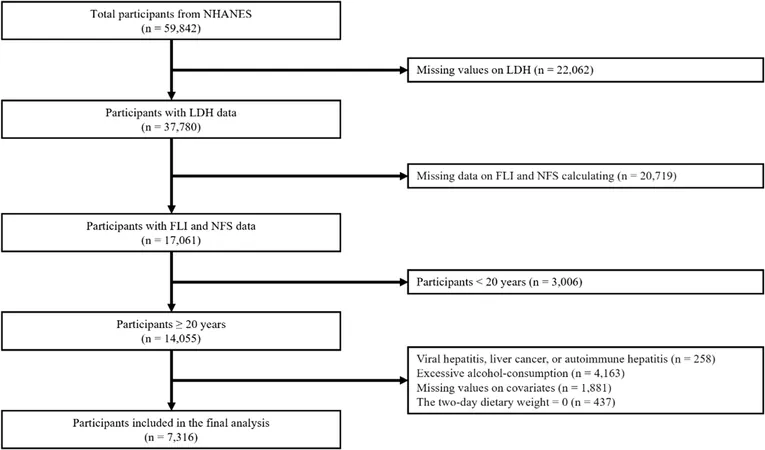
In a recent groundbreaking study analyzing data from 2007 to 2018, researchers focused on a subset of over 59,000 participants to uncover the connection between serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels and conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and advanced hepatic fibrosis (AHF). After implementing specific exclusion criteria, the study narrowed its analysis to 7,316 individuals.
What is Lactate Dehydrogenase?
LDH is an enzyme found in nearly every cell of the body. Its elevated levels can indicate various health issues, particularly in the liver. The study employed a precise method to quantify LDH levels, using advanced laboratory systems to ensure accuracy.
Significance of Indices in Assessing Liver Health
In light of the challenges associated with obtaining liver biopsy samples, researchers turned to the Fatty Liver Index (FLI) and NAFLD Fibrosis Score (NFS) as reliable tools for assessment. Previous studies have validated these indices, proving that higher scores can indicate significant liver health concerns.
Connections Between LDH Levels and Liver Disease
The study revealed striking correlations between elevated LDH levels and both NAFLD and AHF. Initially, higher LDH was linked to an increased risk of liver diseases, a connection that persisted even after accounting for various factors such as age, gender, and lifestyle.
A Closer Look at the Results
As part of the analysis, odds ratios indicated that individuals with elevated LDH faced a significantly higher risk of developing AHF. In fact, the results underscored a potential non-linear relationship, suggesting that as LDH levels rise, so too does the likelihood of serious liver complications.
Key Characteristics of Participants
The study found that younger individuals, those with lower educational levels, and specific demographic groups showed a higher prevalence of liver disease. Notably, those diagnosed with hypertension or diabetes were at an even greater risk.
Implications for Clinical Practice
These findings hold substantial implications for clinical practice. Elevated LDH could serve as a crucial biomarker for early detection and management of liver conditions, guiding healthcare professionals in treatment decisions. Emphasizing lifestyle changes—like improved diet and increased physical activity—could mitigate risks for those at high risk.
The Road Ahead: Research and Recommendations
While this research offers vital insights, it also highlights the need for further studies to elucidate the complexities of liver health, especially regarding NAFLD. Future research should consider a variety of factors, including genetic predispositions and lifestyle choices, all aiming for a deeper understanding of liver disease progression.
Conclusion: Pay Attention to Your Liver!
Understanding the significance of LDH levels could empower individuals to take proactive steps in maintaining liver health. Regular monitoring and awareness of liver-related symptoms might just pave the way for preventing serious health issues down the line. Becoming informed about LDH and its implications may be key to unlocking better health!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)