Unlocking the Secrets of Multiple Myeloma: A Revolutionary Approach to Targeting Tumor Growth
2025-09-17
Author: Sarah
Breaking New Ground in Cancer Research
In the battle against the aggressive blood cancer known as multiple myeloma, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery that could change the treatment landscape forever. A recent study conducted by researchers at Uppsala University reveals that the malignant cells in multiple myeloma differ dramatically from normal cells due to a unique layer of chemical 'tags' that dictate gene behavior. These epigenetic tags hold the key to tumor cell growth and survival, presenting exciting opportunities for new treatment strategies.
Understanding Multiple Myeloma's Challenges
Multiple myeloma is notorious for its ruthless nature, as it leads to a dangerous buildup of malignant plasma cells in the bone marrow. The disease's genetic complexity often gives rise to resistance against standard therapies, resulting in frequent relapses. This underscores an urgent need for innovative therapeutic approaches that can tackle this ruthless cancer head-on.
Mapping the Epigenetic Landscape
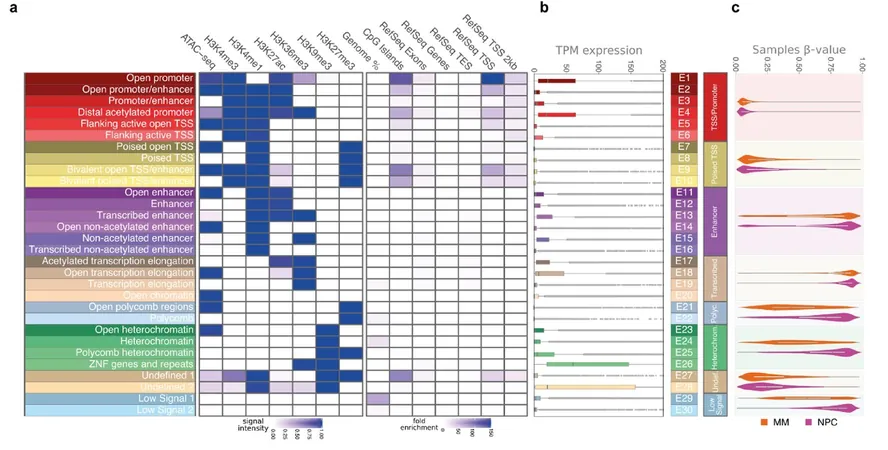
Emerging research has identified epigenetic abnormalities—errors in the chemical tags that regulate gene activity—as critical players in the progression of multiple myeloma. The latest study meticulously maps these epigenetic alterations, contrasting normal plasma cells with their malignant counterparts. According to researcher Antonia Kalushkova, "Our comparisons of samples from myeloma patients and healthy individuals revealed a notable increase in DNA and protein methylation at crucial genomic regions that govern gene activity." This means that the genetic drivers of tumor growth and survival are being manipulated at an unprecedented level.
A Powerful Duo: Targeting Key Enzymes
Another enlightening discovery from the research was the interaction between two key enzymes: DNMT1 and EZH2. Both are staples in the world of epigenetic silencing, and their collaboration presents a tantalizing target for treatment. The team explored the impact of concurrently inhibiting these enzymes and found striking results. By employing a dual approach with an EZH2 inhibitor and a DNMT inhibitor, they sparked significant epigenomic changes and compelling anti-tumor responses.
A New Dawn in Treatment Strategies
The findings suggest that inhibiting both DNMT1 and EZH2 not only reduces harmful DNA methylation but also activates genes linked to cell death, providing a fresh avenue for therapy. Kalushkova emphasizes, "Our results unveil the profound implications of epigenetic gene silencing in the creation of multiple myeloma. The combination of these two strategies could lead to meaningful clinical advances in treatment." This innovative dual approach might just hold the promise of a new era in the fight against multiple myeloma, offering hope to countless patients battling this treacherous disease.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)