Unlocking the Secrets of Medication Use: How Socioeconomic Status and Education Impact Health in Iran
2025-05-19
Author: Jia
The Underexplored Link Between Socioeconomic Factors and Medication Use
When it comes to medication usage, socioeconomic status (SES) and education play pivotal roles, yet their influence at both the individual and community levels is still shrouded in mystery. New research from the PERSIAN cohort sheds light on these associations, revealing fascinating insights into how these factors affect our health.
A Massive Study with Meaningful Results
This groundbreaking study involved data from 163,770 participants aged 35–70 across 18 diverse sites in Iran. By evaluating individual and community SES alongside education levels, researchers employed multi-level analyses to uncover the hidden dynamics shaping medication use and polypharmacy.
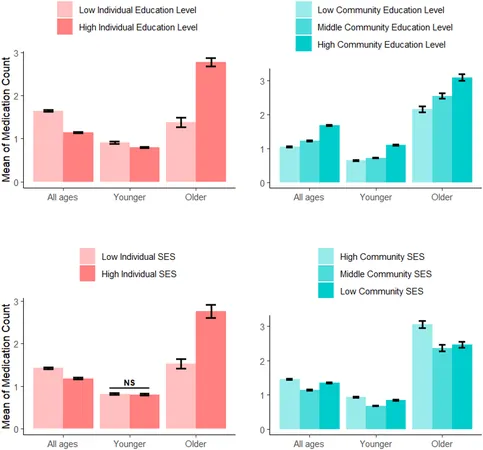
Key Findings: A Mixed Bag for Medication Users
Nearly 45% of respondents reported using at least one medication, averaging 1.32 medications per person, with about 8.85% experiencing polypharmacy. Surprisingly, higher individual SES correlated with increased medication use (PR 1.05), while those living in middle-SES communities exhibited lower medication usage (PR 0.88). Individual education was a double-edged sword; it linked to reduced medication counts (PR 0.92) yet living in highly educated neighborhoods led to increased usage (PR 1.70).
The Complex Role of Education
Higher education often empowers individuals to better manage their health, yet paradoxically, it was also associated with increased healthcare demands in more educated communities. This suggests that while personal education may enhance health literacy, communal education impacts healthcare accessibility and norms.
Why Community Context Matters
One striking conclusion of this study is the significant influence of community-level SES on medication use, highlighting that individuals residing in communities classified as middle SES generally utilized fewer medications. This brings into focus the importance of not only understanding individual circumstances but also the broader community social fabric that shapes health behaviors.
The Implications for Public Health Policy
These findings hold powerful implications for public health strategies targeting both individual behaviors and community health infrastructures. By emphasizing collective health literacy and rational medication use, interventions can be tailored to better suit the nuanced needs of communities across varying socioeconomic backgrounds.
The Road Ahead: Research and Action
While this study offers a wealth of information, its cross-sectional design limits causal interpretations. Future research should delve deeper into the roles of healthcare access, beliefs, and broader socioeconomic indicators to truly unravel the complexities at play. Addressing these issues can pave the way for strategies that promote equitable health access, particularly in underserved regions.
Conclusion: A Call for Community-Focused Health Strategies
Understanding how SES and education influence medication use is vital in shaping effective health policies. This study highlights the need for multifaceted approaches that simultaneously acknowledge individual behaviors and community characteristics, aiming for a healthier future for all.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)