
Unlocking the Secrets of Massive Stars: Expert Astronomer Reveals All!
2024-11-06
Author: Yu
The Formation of Massive Stars
Massive stars, defined as those with eight to over 100 times the mass of our Sun, are born from the intricate process of stellar formation. These luminaries originate in dense clouds of gas and dust throughout interstellar space. The relentless pull of gravity causes these clouds to collapse, forming clumps that become progressively denser and hotter.
Surprisingly, once a star accumulates around 20 solar masses, the intense radiation emitted can create a powerful outward pressure. This force often halts the inflow of surrounding material from the spinning disc, complicating the process of growing even larger. One theory suggests that massive stars tend to form within clusters, where smaller clumps of gas, or protostars, might merge with the primary star, enabling it to achieve colossal size.
What is the Maximum Size a Star Can Reach?
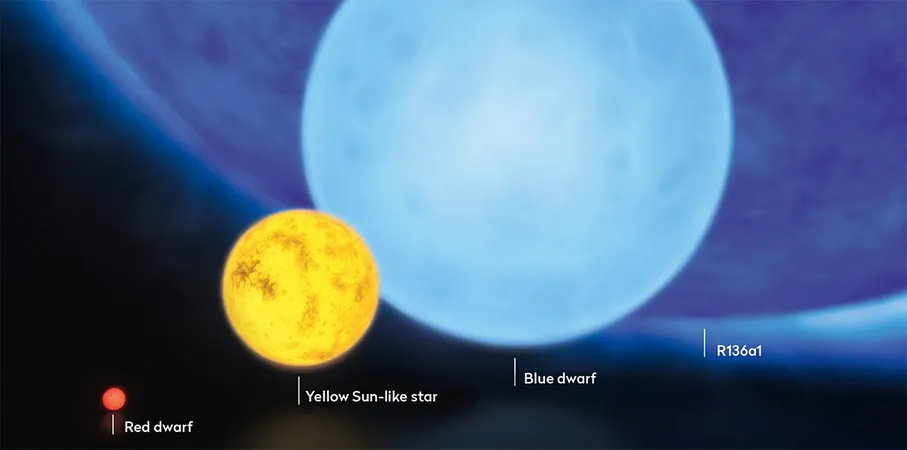
Among the stars that challenge our understanding of size is R136a1, located about 160,000 light-years away in the Tarantula Nebula of the Large Magellanic Cloud. Estimates of its mass range between 170 and 230 solar masses. Astronomers speculate that stars weighing between 150 and 250 solar masses may face instability as they age, leading to spectacular supernova explosions that eject vast quantities of energy and elemental matter into space.
The Life Cycle of Massive Stars vs. Our Sun
The life cycle of a star is heavily influenced by its mass. While our Sun is expected to enjoy a stable existence for around five billion years—eventually expanding into a red giant and leaving behind a white dwarf—a massive star with an initial mass around 20 solar masses will have a dramatically shorter lifespan. It may only endure five million years in a stable phase before transforming into a supergiant and meeting its explosive end in a supernova, ultimately leaving behind either a neutron star or a black hole.
Decoding the Life Cycles of Stars
You might wonder how astronomers are able to chart the life cycles of stars, especially given their prolonged timelines. Instead of observing individual stars over millennia, they take snapshots of entire clusters composed of stars at different evolutionary stages. With the help of advanced techniques like spectroscopy, they gather clues about the varying phases stars pass through, offering insights into the broader narrative of stellar development.
Our Cosmic Connection to Massive Stars
The relationship between humans and massive stars is even more profound than one might think. The essential elements that make up our bodies—like oxygen, silicon, and iron—were created in the fiery cores of these titanic stars or were forged during their cataclysmic supernova explosions. These elements were then scattered across the cosmos, enriching the clouds from which our Solar System and Earth eventually formed. Indeed, we are the stardust of massive stars!
Curious minds, are you eager to learn more about the universe's mysteries or have burning questions about massive stars? The cosmos has much to reveal—dive deeper into the wonders of astrophysics and unlock the secrets of existence!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)