Unlocking the Secrets of Liver Health: How a Simple Weight Loss Can Transform Lives
2025-06-13
Author: Nur
A Groundbreaking Study on Obesity and Liver Disease
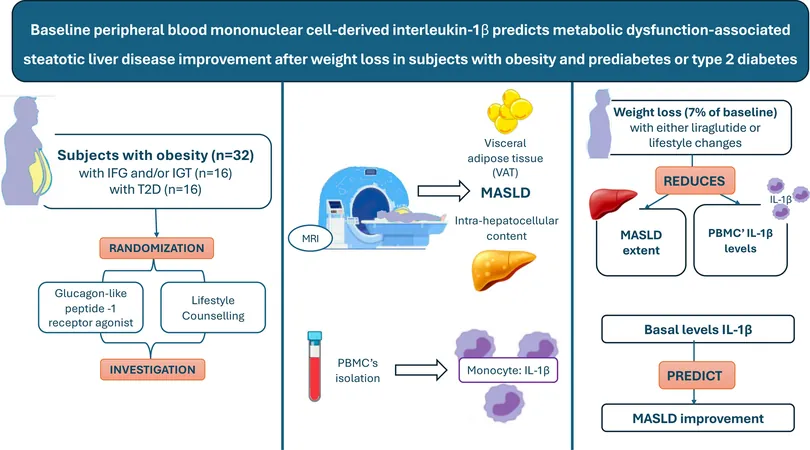
A pivotal study delves into how Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) levels in circulating mononuclear cells may herald improved liver conditions in individuals battling obesity, prediabetes, or type 2 diabetes. The research focused on a select group of 62 obese patients, revealing how a mere 7% weight reduction can yield significant health benefits.
The Journey Begins: Who Was Included?
Participants were meticulously chosen based on specific criteria, including a BMI of 30 or higher and a recent diabetes diagnosis. Notably excluded were individuals with type 1 diabetes, long-term diabetes, or other serious health conditions. The participants underwent a randomized process to receive either liraglutide—a medication aiding in weight loss—or intensive lifestyle counseling.
Innovative Weight Loss Strategies Unveiled
The dual approach involved personalized recommendations for diet and exercise, echoing the principles of the Mediterranean diet. The target? A 7% weight loss goal within 15 months—an amount linked to impressive metabolic improvements. Throughout their journey, participants received regular check-ins and support to keep them motivated.
Unveiling Liver Fat and Cyokine Levels
Using advanced MRI techniques, researchers measured liver fat and monitored levels of IL-1β among participants. Remarkably, findings indicated that those who shed the targeted body weight saw a notable decrease in IL-1β levels—an inflammatory marker pivotal to understanding metabolic conditions.
A Hidden Trigger: The Role of IL-1β
This study underscores the critical role of IL-1β as a biomarker in assessing liver health. Elevated levels of this cytokine were associated with more severe conditions of metabolic associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Through the lens of IL-1β, researchers observed its direct connection to body fat and metabolic health.
Bridging the Gap: From Research to Real-World Impact
The findings shine a light on the urgent need for effective biomarkers that can guide personalized treatment plans for those at risk of liver disease. Given that the process to isolate and measure IL-1β is relatively straightforward and cost-effective, this discovery holds promise for future clinical applications.
Conclusions and Future Directions: A Call to Action
In summary, this groundbreaking study not only reveals how IL-1β levels can predict liver disease improvement after weight loss but also emphasizes the need for increased awareness and targeted strategies in tackling obesity-related health issues. As we look to the future, the implications of this research could be transformative for public health initiatives aimed at curbing the epidemic of liver disease.
Ultimately, the journey from understanding to application will be crucial in shaping the future of liver health and metabolic disease treatment.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)