Unlocking the Secrets of Houttuynia cordata: The Medicinal Marvel Revealed!
2024-12-23
Author: Rajesh
Introduction
Houttuynia cordata, popularly known as yuxingcao, is not just a culinary delight; it has been a cornerstone of traditional medicine for centuries. Revered for its antibiotic-like properties, this plant has been used to address a myriad of ailments ranging from inflammation to respiratory issues. However, the intricate genetic mechanisms that drive its therapeutic capabilities have remained largely uncharted—until now.
Genomic Breakthrough
Researchers at Hunan Agricultural University have taken significant strides in the realm of botanical genomics by successfully sequencing the genome of Houttuynia cordata, a decaploid species. Their groundbreaking findings were published in the esteemed journal Horticulture Research, shedding light on both the genetic blueprint of this medicinal plant and its evolutionary journey. This comprehensive study unveils new insights into the complex biosynthesis of its alkaloids, igniting hope for fully harnessing the plant's medicinal potential.
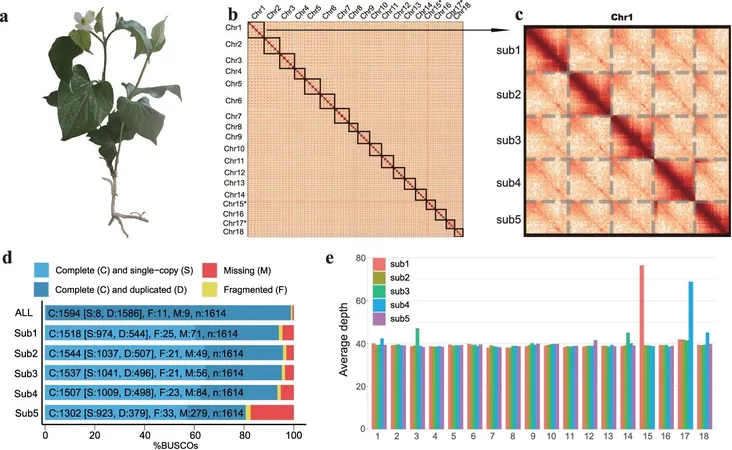
First Chromosome-Scale Reference Genome
The groundbreaking research produced the first chromosome-scale reference genome for Houttuynia cordata, revealing an extensive 2.63 Gb genome comprised of 1,348 contigs, organized into 88 pseudochromosomes. This achievement is no small feat given the daunting challenges researchers face when assembling polyploid genomes.
Whole-Genome Duplication Events
A particularly exciting revelation from the study was the identification of two major whole-genome duplication (WGD) events occurring approximately 17 million and 3.3 million years ago. These duplications appear to have played a significant role in enhancing the plant's adaptability and enriching its repository of medicinal compounds.
Transcriptome Sequencing and Gene Family Expansion
Moreover, by conducting transcriptome sequencing across diverse plant tissues, the research team observed a notable expansion of essential gene families tied to the biosynthesis of isoquinoline and indole alkaloids—well-known for their significant pharmacological properties. These genetic insights lay a robust groundwork for future investigations aimed at bolstering the medicinal efficacy of Houttuynia cordata.
Implications for Future Research
This study marks a significant milestone in our understanding of the genetic intricacies of Houttuynia cordata. By revealing the plant's evolutionary past, we open new avenues for enhancing its medicinal compounds. The genomic data we’ve assembled can become a pivotal resource for future breeding and genetic enhancement efforts.
Conclusion
The implications of this research are monumental—not just for botany but also for modern medicine. The genomic insights gleaned could pave the way for the development of innovative pharmaceuticals. By fine-tuning the plant’s pharmacological properties, Houttuynia cordata has the potential to become a formidable ally in the treatment of respiratory diseases, infections, and other health conditions.
Moreover, this breakthrough research sets the stage for genetic engineering strategies aimed at amplifying the concentration of bioactive compounds within the plant. As the quest for natural medicinal solutions continues to gain traction, the unlocking of Houttuynia cordata's secrets is a thrilling development. Who knows? This ancient herb may hold the key to combating some of today’s most pressing health challenges!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)