
Unlocking the Secrets of Fiery Lava Worlds: A Breakthrough in Exoplanet Science!
2025-08-06
Author: Mei
Astronomers Turn Their Attention to Lava Planets!
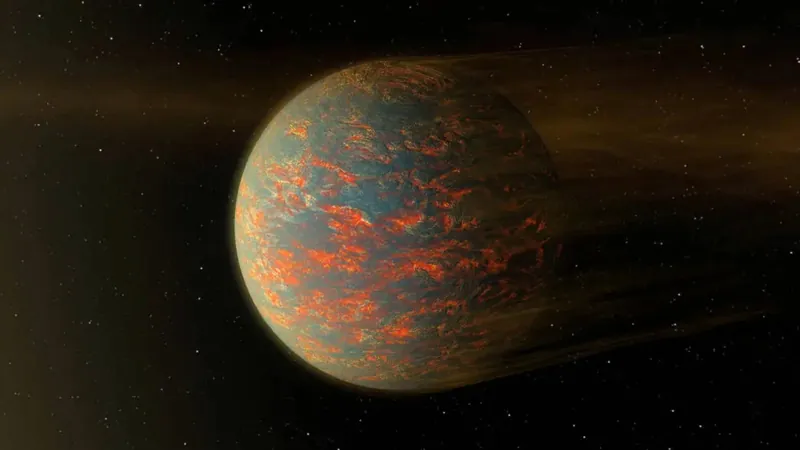
In an exciting leap forward for exoplanet research, astronomers are starting to unravel the mysteries of lava worlds! These unusual planets, which share a similar density to Earth, orbit perilously close to their stars. Their extreme proximity heats them to such scorching temperatures that they melt rocks into possible oceans of magma.
The Challenges of Studying Lava Worlds
While lava planets are a tantalizing new frontier, much remains unclear about their inner workings and evolutionary paths. According to Charles-Édouard Boukari from York University, who co-authored a recent study, the unique orbital configurations of these fiery planets means that traditional knowledge about rocky planets in our solar system doesn’t quite apply. This leaves scientists guessing what might be observed during future explorations.
A Blueprint for Exploring Lava Worlds
With NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) slated to study these exotic worlds, five dedicated programs have been established. Boukari and his team created a conceptual framework—a blueprint—with potential key characteristics of lava planets, including their chemistry and surface conditions. This framework aims to assist astronomers in identifying and analyzing these hot new celestial bodies.
Predicting the Evolution of Lava Planets
Using numerical models, researchers have predicted how lava planets evolve over billions of years, reaching what scientists call a 'thermal steady state.' By blending insights from various scientific fields, the study reveals how the intense internal dynamics of these planets manifest over time.
Molten Beginnings and Unique Features
Interestingly, lava planets may start off molten after formation, similar to magma oceans found in younger planets within our solar system. Yet, despite the extreme heat from their star-facing sides, they solidify at a swift pace. A distinctive feature of lava planets is their long-lasting shallow magma oceans on the sunlit sides, maintaining an ever-shifting chemistry and atmosphere.
A Window Into the Planetary Past
The ongoing crystallization process at the edges of these magma oceans allows scientists to track chemical changes, meaning the atmosphere of older lava planets can provide clues about their age. Researchers believe these planets will have lost most of their volatile substances, leaving behind atmospheres rich in vaporized silicate rocks, which are observable with the JWST.
Understanding Their Evolution Through Temperature
Younger lava planets maintain warmer nightside temperatures of about 1,500 K (1,227 °C) due to internal heat convection. As they age, their nightsides cool significantly. A planet's thermal state can reveal its complex thermochemical history, making temperature measurements vital for understanding planetary evolution.
The Future of Exoplanet Research Is Bright!
With JWST now capable of measuring these critical temperatures, the field of exoplanet science stands poised for exciting discoveries. Upcoming telescopes like the Extremely Large Telescope in Chile will further aid in analyzing the silicate atmospheres of these planets. What began as a hopeful exploration has burgeoned into a new realm of possibilities, giving astronomers the guidelines they need to study this captivating class of extraterrestrial worlds.
A New Era in Exoplanet Observation
The team's innovative predictions have already secured them 100 hours of observation time on the JWST. Boukari expressed hope that distinguishing between old and young lava planets could transform our understanding of exoplanetary science, moving beyond traditional observations.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)