Unlocking the Secrets of Exoplanets: How New Tools Are Revolutionizing Our Understanding of Alien Worlds
2025-07-17
Author: Mei
Discovering Exoplanets with Advanced Climate Models
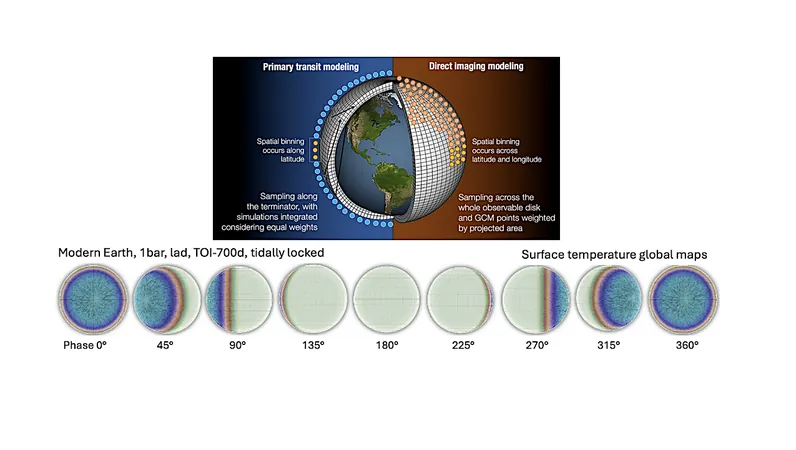
In our relentless pursuit to unveil the mysteries of exoplanets, 3D global climate models (GCMs) have emerged as transformative tools. These models are crucial for predicting atmospheric conditions, creating a dynamic interplay between observation and simulation that deepens our grasp of distant worlds.
Introducing the Global Emission Spectra (GlobES)
This groundbreaking research introduces the Global Exoplanet Spectra (GlobES) module, a vital component of the Planetary Spectrum Generator (PSG). It seamlessly integrates atmospheric and surface data, providing scientists with a powerful, user-friendly resource to analyze the atmospheres of various planets.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Exploring exoplanets like TRAPPIST-1 b, TRAPPIST-1 e, and Earth, this innovative tool showcases its prowess in generating simulations of transit, emission, and reflected spectra. This capability not only enhances our understanding but also supports cutting-edge missions like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and concepts such as the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO).
The Science of Light: Ray-Tracing Through Atmospheres
One of the fascinating aspects addressed in this research is the ray-tracing technique through planetary atmospheres. This method captures the nuanced variations of light paths as they curve and refract within the atmospheric layers. As a result, observers can distinguish the source of detected radiation, whether from a surface, the top of the atmosphere (TOA), or a background star.
Meet the Visionaries Behind the Research
This transformative research is driven by a team of experts: Thomas J. Fauchez, Geronimo L. Villanueva, Vincent Kofman, Gabriella Suissa, and Ravi K. Kopparapu. Their dedication to unraveling the complexities of exoplanet atmospheres promises to propel our understanding of the cosmos forward.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)