Unlocking the Secrets of Exoplanet Biosignatures: A Breakthrough in Machine Learning
2025-04-05
Author: Arjun
The quest to find signs of life beyond our solar system hinges upon one major challenge: identifying atmospheric biosignatures on Earth-like exoplanets. This task is far from simple, considering the need for high-resolution observations and prolonged data collection to detect biogenic gases present in terrestrial atmospheres.
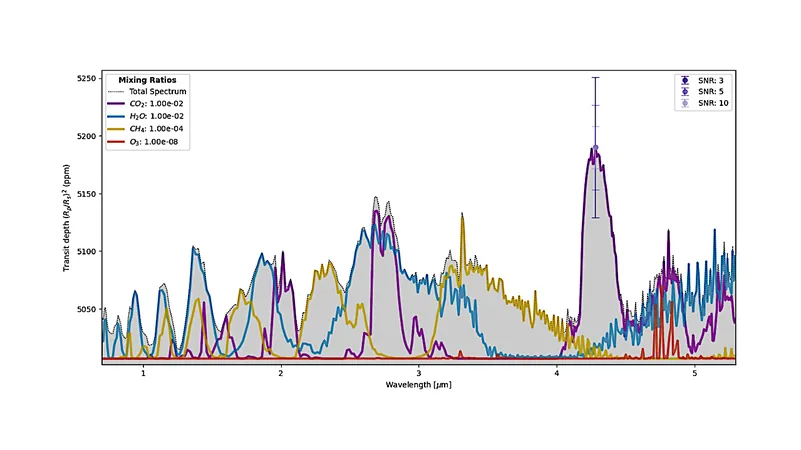
In a groundbreaking research effort, scientists have developed a novel machine-learning methodology aimed specifically at classifying transmission spectra that are plagued by low Signal-to-Noise Ratios (SNR). This innovative approach allows researchers to differentiate between spectra that may contain vital biosignatures, including methane, ozone, and water, and those that warrant further investigation.
To achieve this, a comprehensive dataset comprising approximately 1 million synthetic spectra was generated, mimicking environments of planets akin to TRAPPIST-1 e. These synthetic spectra were created using a specialized software package called MultiREx. The results were striking: the machine-learning models demonstrated an impressive ability to classify transmission spectra with SNR values lower than 6, successfully identifying those enriched with methane and ozone at levels comparable to both modern and ancient Earth environments.
Remarkably, these trained models also proved effective on realistic synthetic spectra based on current Earth's atmosphere. In fact, under the right conditions, one of the models indicated a high probability of detecting biosignatures from many inhabited terrestrial planets currently being observed by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and its NIRSpec PRISM instrument, especially around nearby M-dwarfs like those in the TRAPPIST-1 system.
The implications of this research extend beyond a mere academic exercise; it has the potential to revolutionize the planning and execution of astronomical observation programs. By incorporating machine-assisted strategies similar to those developed in this study, scientists can significantly enhance the utilization of JWST resources, improving the prospects for discovering signs of extraterrestrial life through targeted follow-up observations on promising candidates.
With the cosmos still shrouded in mystery, advancements in machine learning are setting the stage for a new era of exploration. As we stand on the threshold of potentially monumental discoveries that could answer the age-old question of whether we are alone in the universe, this technology may be our key to unraveling the secrets of biosignatures in distant worlds. Stay tuned as we continue to follow the extraordinary journey of astrobiology and the search for life beyond Earth!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)